This repository presents a selection of data from a masters thesis project which can be accessed here.
High Performance Liquid Chromatography was performed to generate metabolic data that corresponded with cocatalyst growth. This repository houses the raw metabolic data that was collected for this project.
The R script used to visualize the metabolic data is shown here with the respective outputs displayed in Rmarkdown.
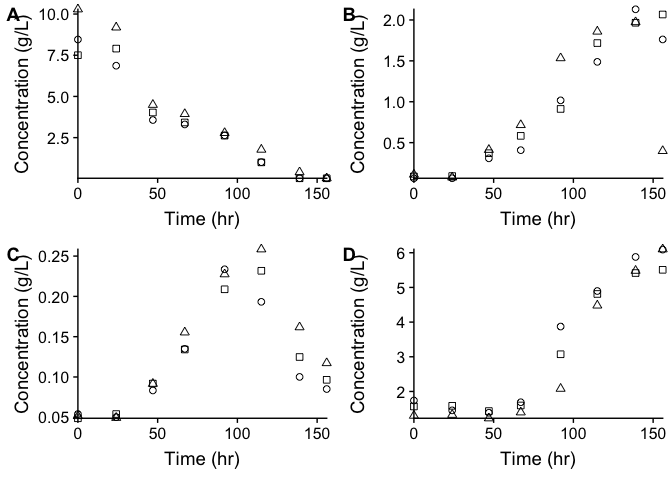
The graphs below display the substrate consumed and metabolites produced by a novel coculture of Propionibacterium freudenreichii ssp. shermanii and Geobacter sulfurreducens. This particular coculture was developed for use as an anodic biocatalyst in microbial fuel cells. Specifically, to address the low power generation that impedes the advancement of microbial fuel cell technology. While Propionibacterium freudenreichii ssp. shermanii has shown potential as a biocatalyst, its incomplete consumption of the anodic substrate is a persistent issue. This project as a whole aimed to optimize substrate consumption to increase power generation using Propionibacterium freudenreichii ssp. shermanii as a biocatalyst. The effect of coculturing Geobacter sulfurreducens with Propionibacterium freudenreichii ssp. shermanii was investigated. The cocatalyst and pure culture performance was tested in an air-cathode microbial fuel cell and the metabolic data is presented in this repository. The novel cocatalyst was shown to produce electricity, however a full characterization to elucidate the contribution to power generation by each microbe would be desirable to investigate.
Figure - HPLC results for cocatalyst P. shermanii and G. sulfurreducens fermentation trials and triplicate experiments are shown. Figures A, B, C and D correspond to concentrations of glucose, acetate, succinate and propionate respectively.