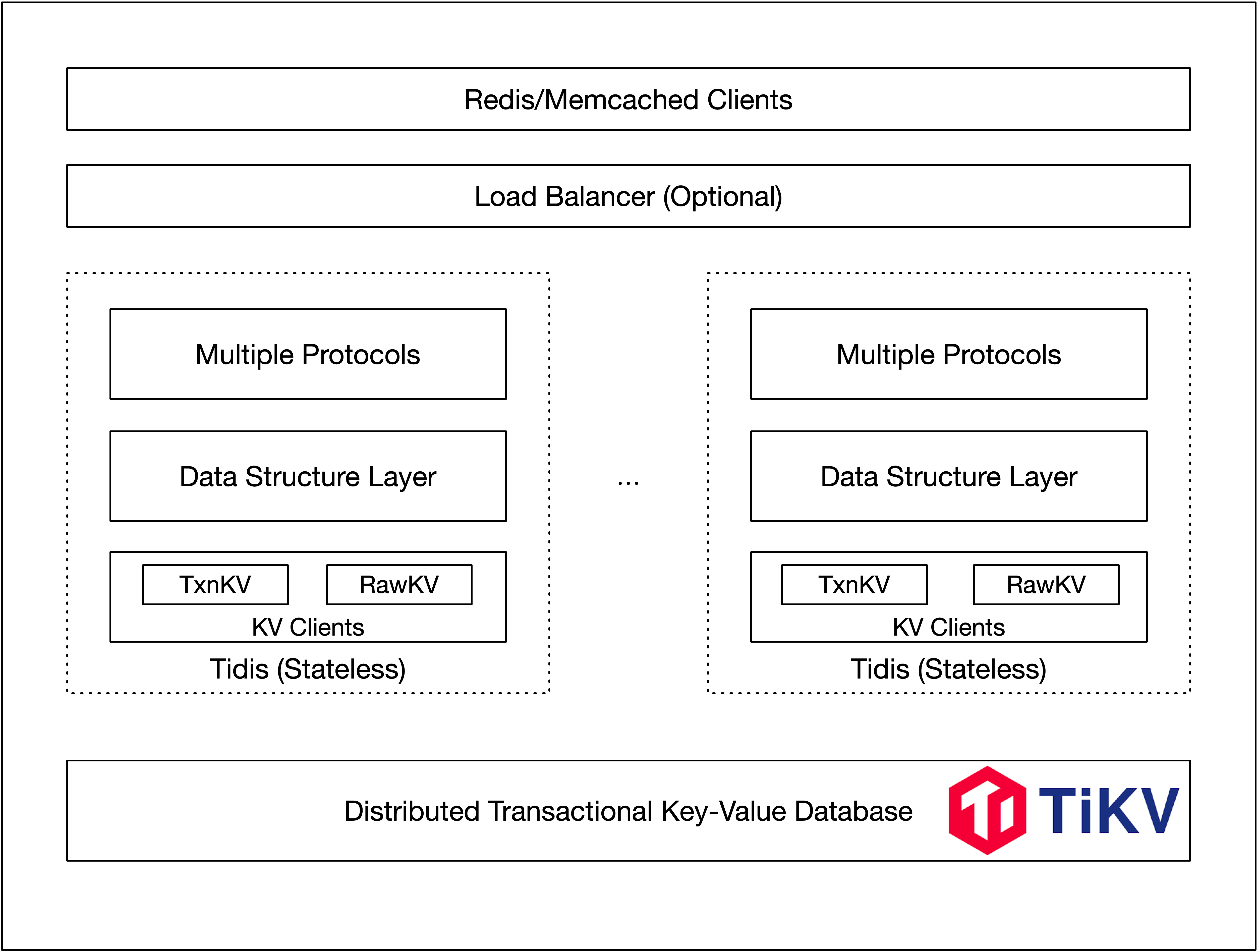
Tidis is the service layer for TiKV, aims to provide redis protocol compatiable distributed storage service powered by PingCAP. Redis protocol has been implemented with multiple datatypes (string/hash/list/set/sortedset) support.
Tidis has been completely redesigned and rewritten in Rust for better performance and lower latency, and added more important features, such as Lua scripts, TLS connections, lock optimization and more.
Redis is an in-memory data structure store, used by lots of companies and projects. It is a very good solution for caching and storing data. But it has some limitations:
- High cost of memory, not suitable for store huge amounts of data
- Not easy to manage, and not easy to scale out with huge datasets
- Lots of use cases are relying on protocol and api, not the extreme performance
- No global transaction support
- No data persistence guarantee
We believe it is a good idea to build a redis compatiable distributed storage service based on lower cost storage medium. Further more, there are popular products built with this idea, such as ssdb, pika, kvrocks and so on. But they are all compute storage aggregated architechture, which means it's very complex and complicated to build the basic ability of storage replication, high availability, data sharding, data scaling and so on. Not only it is difficult to implement, but also complicated to operate in production.
Considering the complexities, we take a different approach and build a lite computing service layer on top of TiKV, a distributed storage system based on Raft consensus algorithm. TiKV is an excellent building block for storage systems, it has a lot of features such as high availability, data sharding, data scaling, global transaction and so on. We just work on the data model and computation which is also known as the service layer.
Of course we are not the only ones who have similar ideas. Both Titan and Tidis 1.0 were designed with similar architecture, and they were all popular back to early days and grew their community to some extent. Unfortunately, there are many useful features not implemented by either of them. We believe the community is always looking forward to seeing alternative projects that are more feature complete. Therefore we decided to take over what Tidis 1.0 left behind, redesign and implement the next generation of Tidis with some important yet missing features added, such as Lua script, TLS/SSL, lock optimization, one phase commit, asynchronous commit and many other improvements.
- Multiple protocols support
- Linear scale-out
- Storage and compute disaggregation
- Highly durable and available with strong consistency
- Global transaction support
Architechture of Tidis
Architechture of TiKV
- Placement Driver (PD): PD is the brain of the TiKV system which manages the metadata about Nodes, Stores, Regions mapping, and makes decisions for data placement and load balancing. PD periodically checks replication constraints to balance load and data automatically.
- Node: A physical node in the cluster. Within each node, there are one or more Stores. Within each Store, there are many Regions.
- Store: There is a RocksDB within each Store and it stores data in local disks.
- Region: Region is the basic unit of Key-Value data movement and corresponds to a data range in a Store. Each Region is replicated to multiple Nodes. These multiple replicas form a Raft group. A replica of a Region is called a Peer.
-
Start
PD,TiKVand oneTiDB(for trigger GC) usingTiUP, you can follow the official instructions English or 中文. -
Build the Tidis server
make release
- Start the Tidis server
tidis-server --config config.toml
You can use the demo configuration below.
[server]
listen = "0.0.0.0"
port = 6379 # disable tcp port if set to 0
tls_listen = "0.0.0.0"
tls_port = 6443 # disable tls if tls_port set to 0
tls_key_file = "" # disable tls if key or cert file not set
tls_cert_file = ""
tls_auth_client = false # tls_ca_cert_file must be specified if tls_auth_client is true
tls_ca_cert_file = "path/ca.crt"
pd_addrs = "127.0.0.1:2379" # PD addresses of the TiKV cluster
instance_id = "1" # instance_id can be used as tenant identifier
prometheus_listen = "0.0.0.0"
prometheus_port = 8080
log_level = "info"
log_file = "tidis.log"
[backend]
use_txn_api = true # use transaction api for full api supported
use_async_commit = true # try to use async commit in tikv
try_one_pc_commit = true # try to use one pc commit
use_pessimistic_txn = true # use optimistic transaction mode
local_pool_number = 4 # localset pool number for handle connections
txn_retry_count = 10 # transaction retry count
txn_region_backoff_delay_ms = 2 # transaction region error backoff base delay time
txn_region_backoff_delay_attemps = 2 # transaction region error backoff retry max attempts
txn_lock_backoff_delay_ms = 2 # transaction lock error backoff base delay time
txn_lock_backoff_delay_attemps = 5 # transaction lock error backoff retry max attempts- Run clients
For the redis protocol, you can use the official redis clients, such as redis-cli.
redis-cli -p 6379
tidis> SET mykey "Hello"
"OK"
tidis> GET mykey
"Hello"
tidis> EXPIRE mykey 10
(integer) 1
# 10 seconds later
tidis> GET mykey
(nil)
tidis> RPUSH mylist "one"
(integer) 1
tidis> RPUSH mylist "two"
(integer) 2
tidis> RPUSH mylist "three"
(integer) 3
tidis> LRANGE mylist 0 0
1) "one"
tidis> LRANGE mylist -3 2
1) "one"
2) "two"
3) "three"
tidis> LRANGE mylist -100 100
1) "one"
2) "two"
3) "three"
tidis> LRANGE mylist 5 10
(nil)
tidis> ZADD myzset 1 "one"
(integer) 1
tidis> ZADD myzset 2 "two"
(integer) 1
tidis> ZADD myzset 3 "three"
(integer) 1
tidis> ZREMRANGEBYSCORE myzset 0 1
(integer) 1
tidis> ZRANGE myzset 0 5 WITHSCORES
1) "two"
2) "2"
3) "three"
4) "3"
+-----------+-------------------------------------+
| pexpire | pexpire key int |
+-----------+-------------------------------------+
| pexpireat | pexpireat key timestamp(ms) |
+-----------+-------------------------------------+
| expire | expire key int |
+-----------+-------------------------------------+
| expireat | expireat key timestamp(s) |
+-----------+-------------------------------------+
| pttl | pttl key |
+-----------+-------------------------------------+
| ttl | ttl key |
+-----------+-------------------------------------+
| type | type key |
+-----------+-------------------------------------+
| scan | scan "" [count 10] [match "^pre*"] |
+-----------+-------------------------------------+
| ping | ping |
+-----------+-------------------------------------+
+-----------+-------------------------------------+
| command | format |
+-----------+-------------------------------------+
| get | get key |
+-----------+-------------------------------------+
| set | set key value [EX sec|PX ms][NX|XX] |
+-----------+-------------------------------------+
| del | del key1 key2 ... |
+-----------+-------------------------------------+
| mget | mget key1 key2 ... |
+-----------+-------------------------------------+
| mset | mset key1 value1 key2 value2 ... |
+-----------+-------------------------------------+
| incr | incr key |
+-----------+-------------------------------------+
| incrby | incr key step |
+-----------+-------------------------------------+
| decr | decr key |
+-----------+-------------------------------------+
| decrby | decrby key step |
+-----------+-------------------------------------+
| strlen | strlen key |
+-----------+-------------------------------------+
+------------+------------------------------------------+
| Commands | Format |
+------------+------------------------------------------+
| hget | hget key field |
+------------+------------------------------------------+
| hstrlen | hstrlen key field |
+------------+------------------------------------------+
| hexists | hexists key field |
+------------+------------------------------------------+
| hlen | hlen key |
+------------+------------------------------------------+
| hmget | hmget key field1 field2 field3... |
+------------+------------------------------------------+
| hdel | hdel key field1 field2 field3... |
+------------+------------------------------------------+
| hset | hset key field value |
+------------+------------------------------------------+
| hsetnx | hsetnx key field value |
+------------+------------------------------------------+
| hmset | hmset key field1 value1 field2 value2... |
+------------+------------------------------------------+
| hkeys | hkeys key |
+------------+------------------------------------------+
| hvals | hvals key |
+------------+------------------------------------------+
| hgetall | hgetall key |
+------------+------------------------------------------+
| hincrby | hincrby key step |
+------------+------------------------------------------+
+------------+---------------------------------------------+
| commands | format |
+------------+---------------------------------------------+
| lpop | lpop key |
+------------+---------------------------------------------+
| rpush | rpush key item |
+------------+---------------------------------------------+
| lpush | lpush key item |
+------------+---------------------------------------------+
| rpop | rpop key |
+------------+---------------------------------------------+
| llen | llen key |
+------------+---------------------------------------------+
| lindex | lindex key index |
+------------+---------------------------------------------+
| lrange | lrange key start stop |
+------------+---------------------------------------------+
| lset | lset key index value |
+------------+---------------------------------------------+
| ltrim | ltrim key start stop |
+------------+---------------------------------------------+
| linsert | linsert key <BEFORE | AFTER> pivot element |
+------------+---------------------------------------------+
+-------------+-------------------------------------+
| commands | format |
+-------------+-------------------------------------+
| sadd | sadd key member1 [member2 ...] |
+-------------+-------------------------------------+
| scard | scard key |
+-------------+-------------------------------------+
| sismember | sismember key member |
+-------------+-------------------------------------+
| smismember | smismember key member [member2 ...] |
+-------------+-------------------------------------+
| smembers | smembers key |
+-------------+-------------------------------------+
| srem | srem key member |
+-------------+-------------------------------------+
| spop | spop key [count] |
+-------------+-------------------------------------+
| srandmember | spop key [count] |
+-------------+-------------------------------------+
+------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------+
| commands | format |
+------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------+
| zadd | zadd key member1 score1 [member2 score2 ...] |
+------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------+
| zcard | zcard key |
+------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------+
| zrange | zrange key start stop [WITHSCORES] |
+------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------+
| zrevrange | zrevrange key start stop [WITHSCORES] |
+------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------+
| zrangebyscore | zrangebyscore key min max [WITHSCORES][LIMIT offset count] |
+------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------+
| zrevrangebyscore | zrevrangebyscore key max min [WITHSCORES][LIMIT offset count] |
+------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------+
| zremrangebyscore | zremrangebyscore key min max |
+------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------+
| zremrangebyrank | zremrangebyscore key start stop |
+------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------+
| zcount | zcount key |
+------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------+
| zscore | zscore key member |
+------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------+
| zrank | zrank key member |
+------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------+
| zrem | zrem key member1 [member2 ...] |
+------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------+
| zpopmin | zpopmin key [count] |
+------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------+
| zpopmax | zpopmax key [count] |
+------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------+
| zincrby | zincrby key increment member |
+------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------+
+-------------+-----------------------------------------------------+
| commands | format |
+-------------+-----------------------------------------------------+
| eval | eval script numkeys [key [key ...]] [arg [arg ...]] |
+-------------+-----------------------------------------------------+
| evalsha | evalsha sha1 numkeys [key [key ...]] [arg [arg ...]]|
+-------------+-----------------------------------------------------+
| script load | script load script |
+-------------+-----------------------------------------------------+
| script flush| script flush |
+-------------+-----------------------------------------------------+
|script exists| script exists sha1 [sha1 ...] |
+-------------+-----------------------------------------------------+
+-------------+----------------------+
| commands | format |
+-------------+----------------------+
| auth | auth password |
+-------------+----------------------+
+-------------+----------------------+
| commands | format |
+-------------+----------------------+
| debug | debug profiler_start |
+-------------+----------------------+
| debug | debug profiler_stop |
+-------------+----------------------+
+-----------------+------------+
| command | support |
+-----------------+------------+
| cluster nodes | Yes |
+-----------------+------------+
| cluster info | Yes |
+-----------------+------------+
+---------+---------+
| command | support |
+---------+---------+
| multi | Yes |
+---------+---------+
| exec | Yes |
+---------+---------+
| discard | Yes |
+---------+---------+
+-----------------+------------+
| command | support |
+-----------------+------------+
| client setname | Yes |
+-----------------+------------+
| client getname | Yes |
+-----------------+------------+
| client id | Yes |
+-----------------+------------+
| client list | Yes |
+-----------------+------------+
| client kill | Yes |
+-----------------+------------+
You can run complete sets of all supported commands using the tools provided in the repo test directory, just run
python3 test_helper.py [--ip ip] [--port 6379]
TLS/SSL encryption is necessary for security, especially in public access environment, such as providing cloud services in AWS, GCP or Azure cloud.
Tidis support one-way and two-way TLS authentication handshake. In one-way authentication, you can use the ca certificate and password for security transport and authenticate. If you choose two-way authentication, it is safe using ca certificate with client-side key and certificate without password.
#!/bin/bash
# Generate some test certificates which are used by the regression test suite:
#
# tests/tls/ca.{crt,key} Self signed CA certificate.
# tests/tls/redis.{crt,key} A certificate with no key usage/policy restrictions.
# tests/tls/client.{crt,key} A certificate restricted for SSL client usage.
# tests/tls/server.{crt,key} A certificate restricted for SSL server usage.
generate_cert() {
local name=$1
local cn="$2"
local opts="$3"
local keyfile=tests/tls/${name}.key
local certfile=tests/tls/${name}.crt
[ -f $keyfile ] || openssl genrsa -out $keyfile 2048
openssl req \
-new -sha256 \
-subj "/O=Redis Test/CN=$cn" \
-key $keyfile | \
openssl x509 \
-req -sha256 \
-CA tests/tls/ca.crt \
-CAkey tests/tls/ca.key \
-CAserial tests/tls/ca.txt \
-CAcreateserial \
-days 365 \
$opts \
-out $certfile
}
mkdir -p tests/tls
[ -f tests/tls/ca.key ] || openssl genrsa -out tests/tls/ca.key 4096
openssl req \
-x509 -new -nodes -sha256 \
-key tests/tls/ca.key \
-days 3650 \
-subj '/O=Redis Test/CN=Certificate Authority' \
-out tests/tls/ca.crt
cat > tests/tls/openssl.cnf <<_END_
[ server_cert ]
keyUsage = digitalSignature, keyEncipherment
nsCertType = server
[ client_cert ]
keyUsage = digitalSignature, keyEncipherment
nsCertType = client
_END_
generate_cert server "Server-only" "-extfile tests/tls/openssl.cnf -extensions server_cert"
generate_cert client "Client-only" "-extfile tests/tls/openssl.cnf -extensions client_cert"
generate_cert redis "Generic-cert"- Server-side
tls_listen = "0.0.0.0"
tls_port = 6443
tls_key_file = "path/server.key"
tls_cert_file = "path/server.crt"
tls_auth_client = false # tls_ca_cert_file must be specified if tls_auth_client is true
tls_ca_cert_file = "path/ca.crt"- Client-side
tls_auth_client is false, client just use root ca certificate
./src/redis-cli --tls --cacert ./tests/tls/ca.crttls_auth_client is true, client must be configure certs and key file for client auth in server side
./src/redis-cli --tls --cert ./tests/tls/client.crt --key ./tests/tls/client.key --cacert ./tests/tls/ca.crtThanks to the global transaction mechanism in TiKV cluster, Tidis can support global transaction easily. Use MULTI/EXEC/DISCARD command just like Redis Cluster but without caring about the CROSSSLOT error, just use it like a single Redis instance.
In Tidis, there are two kinds of transaction models, optimistic and pessimistic models.
Pessimistic transaction is prefered when you have many concurrent writes to limited hot keys. Otherwise, you should use optimistic transaction instead for better performance.
You can refer to the documents in TiDB optimistic transaction and pessimistic transaction.
In addition, the 1pc and async commit options are helpful for better performance in most use cases. You can refer to the documents in PingCAP blog AsyncCommit, the Accelerator for Transaction Commit in TiDB 5.0 for details.
Tidis use mlua library to interpret lua scripts. We can use EVAL/EVALSHA to execute lua script with global transaction support, without caring about the CROSSSLOT error either.
The lua script will be running in a new transaction context, so all read and writes in the lua script are guaranteed to be atomic.
All lua script e2e test cases are located in test/test_lua.py.
For collection keys with thousands of items, deletion can be a time-consuming operation, enable the async deletion configuration could greatly reduce the operation time.
The big key deletion task will run in background and response to user immediately without waiting for the background task's completion. We maintain multiple versions of the same key if the old version has been deleted in asynchronous way. If there are pending deletes with old versions, next new version of the key will be monotonic increase from the largest version of the key. Otherwise, the new version will start from 0.
For big keys with thousands of elements deletion, the time spent decrease from seconds to milliseconds.
| type | hash | list | set | sorted set |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| sync deletion | 1.911778 s | 2.047429 s | 2.145035 s | 4.892823 s |
| async deletion | 0.005159 s | 0.004694 s | 0.005370 s | 0.005403 s |
Enable super batch could have significant performance benefits, and you can tune it based on your real workload.
Super batch is a feature that can reduce the number of request round-trips to TiKV. It is enabled by default, and can be disabled by setting to allow_batch=false in the configuration file. There are more configuration options available for advanced tuning. max_batch_wait_time is the maximum waiting time for a batch, and max_batch_size is the maximum number of keys in one batch. overload_threshold is the threshold of the backend TiKV server's load, if the load is higher than this value, the batch request will be sent immediately.
You can tune the parameters according to your workload. In the following test, we set max_batch_wait_time to 10ms, overload_threshold to 0, and max_batch_size varies. The test result shows that the throughput increases 50% and p999 latency decreases 40% with max_batch_size=20.
The topology of cluster to run benchmark has 3 TiKV nodes, 3 Tidis nodes, 1 PD node and 1 TiDB node (for gc). We benchmark the cluster using multiple memtier-benchmark processes, with various number of parallel connections. The benchmark result shows the max read and write throughput are 540k ops/s and 125k op/s respectively.
The latency distribution shows that the latency will increase when the cluster load reaches to a certain limit. The p9999 latency increased significantly with 1200 concurrent connections, up to 47ms.
We also compared the benchmark result with other similar Redis on TiKV projects (Titan and Tidis 1.0), the result shows that Tidis has better write throughput than Titan and Tidis 1.0.
The write thoughput of Tidis is almost twice of Titan and Tidis 1.0 and the latency are the best all the time.
See more Benchmark details here.
Tidis is under the Apache-2.0 license. See the LICENSE file for details.