Mobina Moeini 1, Rouhollah Ahmadian 1, Mehdi Ghatee 1
1Amirkabir University of Technology
If you use our method, please cite it by:
@inproceedings{moeini2024calibrated,
title={Calibrated SVM for Probabilistic Classification of In-Vehicle Voices into Vehicle Commands via Voice-to-Text LLM Transformation},
author={Moeini, Mobina and Ahmadian, Rouhollah and Ghatee, Mehdi},
booktitle={2024 8th International Conference on Smart Cities, Internet of Things and Applications (SCIoT)},
pages={180--188},
year={2024},
organization={IEEE}
}
Welcome to the Digital Voice Command Recognition System in-car project! This repository hosts the source code and resources for a voice command recognition system that utilizes machine learning and natural language processing techniques to identify car-related commands from the audio input.
The Voice Command Recognition System aims to recognize and classify commands from audio recordings. The system can distinguish between various predefined commands, such as opening doors, windows, or Bluetooth connections, controlling the steering wheel, and more. The project utilizes a combination of natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning (ML) techniques to achieve accurate and reliable command recognition.
In this project, in-vehicle commands of this dataset have been used.
-
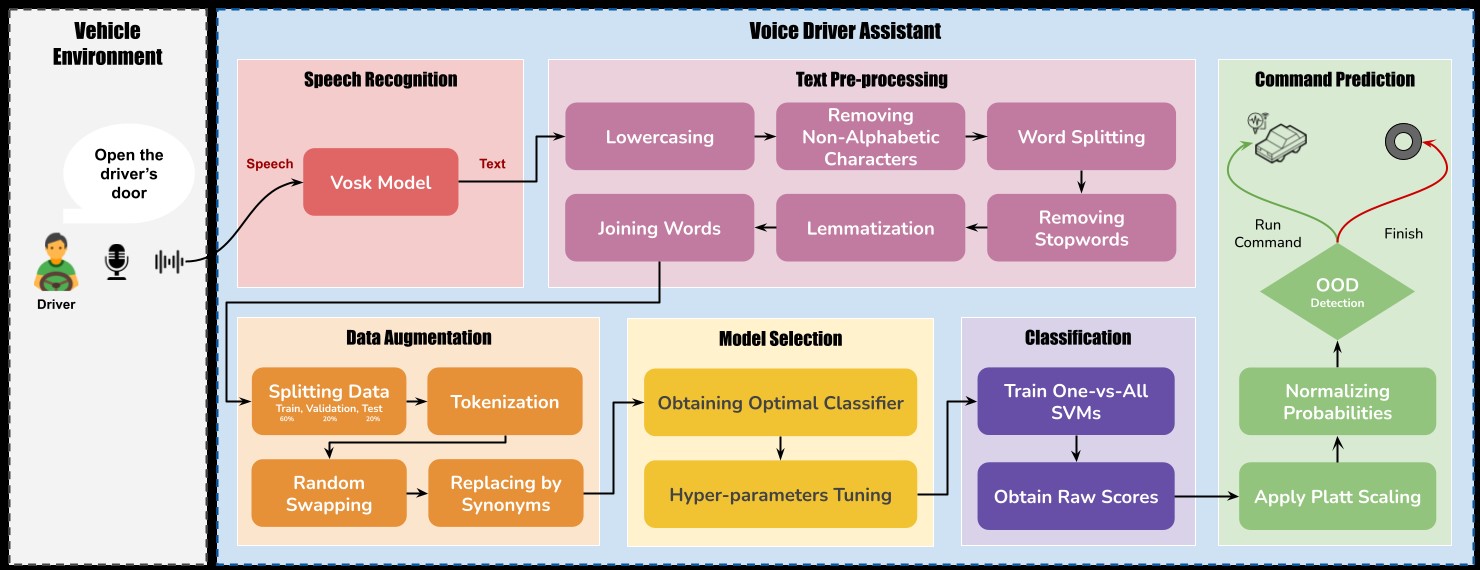
Speech Recognition: The system is capable of capturing audio input from a microphone, making it suitable for real-world scenarios where voice commands need to be recognized instantly. Utilizing the advanced Vosk deep learning model, spoken input is accurately transformed into text for further processing within the system
-
Command Classification: Using machine learning models, the system classifies input text into predefined categories, enabling precise command recognition.
-
Unknown Command Handling: The system includes the ability to handle unknown or ambiguous commands by assigning them a specific "Unknown" label, ensuring robustness and adaptability.
-
Speech Recognition: We leverage the open-source Vosk model for speech recognition, ensuring accurate transcription of spoken user input into text format. Vosk stands out for its offline functionality, high accuracy, and multilingual support. What sets Vosk apart is its ease of customization.
-
Data Preprocessing: Preprocessing techniques included lowercasing, tokenization, lemmatization, and the removal of numbers, contractions, empty strings, and stop words. These techniques aimed to standardize the data format and remove irrelevant information that could hinder model performance. These pre-processing techniques helped filter noise, reduce sparsity, and enhance the semantic content extracted from the text. The uniformly pre-processed data served as input for subsequent model training and evaluation in the classification phase of the proposed framework.
-
Data Augmentation: To address our dataset's limitations, we employ augmentation techniques like random swapping and synonym replacement. These methods expand the training set and mitigate overfitting risks.
-
Model Training: Various Machine learning models such as MLP, Logistic Regression, RandomForest, GradientBoosting, and SVM are trained on our dataset and the best ones are chosen by comparing the classification results. Support Vector Machine (SVM) was chosen as the best model and trained on the preprocessed data to learn the patterns associated with each command.
-
Real-Time Recognition: The system captures and processes audio in real-time, predicting the spoken command using the trained models.
- Clone this repository to your local machine.
- Install the required dependencies using the provided
requirements.txtfile. - Run the system.
- Enhanced Command Set: Expand the range of recognized commands to cover a wider spectrum of user interactions.
- Multilingual Support: Extend the project to handle commands and instructions in multiple languages. This would require translating and preprocessing text in various languages while maintaining the model's accuracy.
- Continuous Learning: Explore techniques to enable the system to learn new commands from user input, enhancing adaptability.
- Collaborative Filtering: Implement collaborative filtering techniques to learn from the preferences of different users and adapt the model accordingly.
- Utilizing Pre-trained Language Models (LLMS): Explore the utilization of pre-trained Large Language Models for Transfer Learning to improve the efficiency of the text classification model, especially in scenarios characterized by limited labeled data.
Contributions are welcome! If you find issues or have suggestions for improvements, feel free to create pull requests or open issues in this repository.