PyTorch lets you send a model or tensor .to(device), so
why can't you do my_fn.to('a_gcp_a100') or my_table.to('parquet_in_s3')?
Runhouse allows just that: send code and data to any of your compute or
data infra (with your own cloud creds), all in Python, and continue to interact with
them normally from your existing code and environment. Think of it as an expansion pack to your Python
interpreter that lets it take detours to remote machines or manipulate remote
data. It wraps industry-standard tooling like Ray, gRPC, and the Cloud SDKs (boto, gsutil, etc. via SkyPilot)
to give you production-quality features like queuing, distributed, async, logging,
low latency, auto-launching, and auto-termination out of the box.
Runhouse is for ML Researchers, Engineers, and Data Scientists who are tired of:
- 🚜 manually shuttling code and data around between their local machine, remote instances, and cloud storage,
- 🐜 debugging over ssh and notebook tunnels,
- 🧑🔧 translating their code into a pipeline DSL just to use multiple hardware types,
- 🪦 debugging in an orchestrator,
- 👩
✈️ missing out on fancy LLM IDE features, - 🕵️ and struggling to find or reproduce their teammates' code and data artifacts.
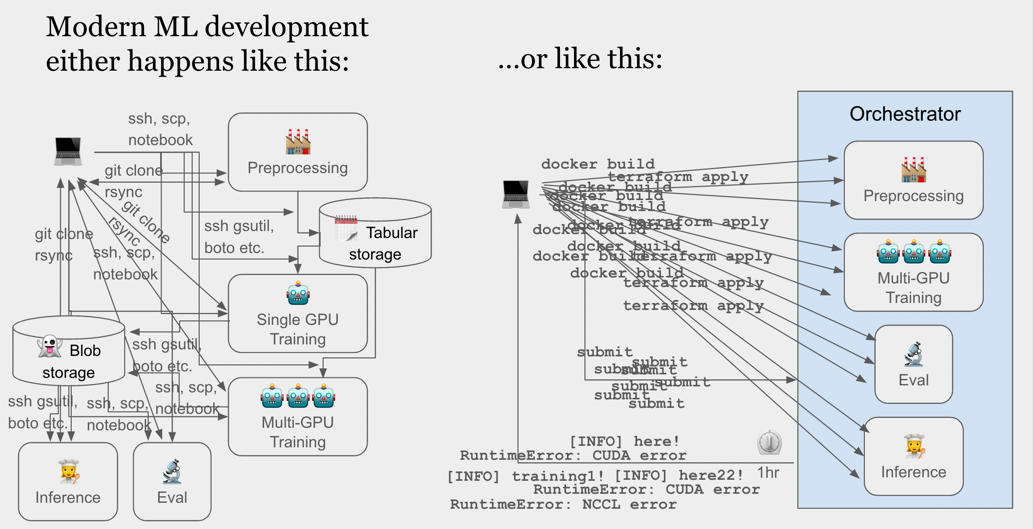
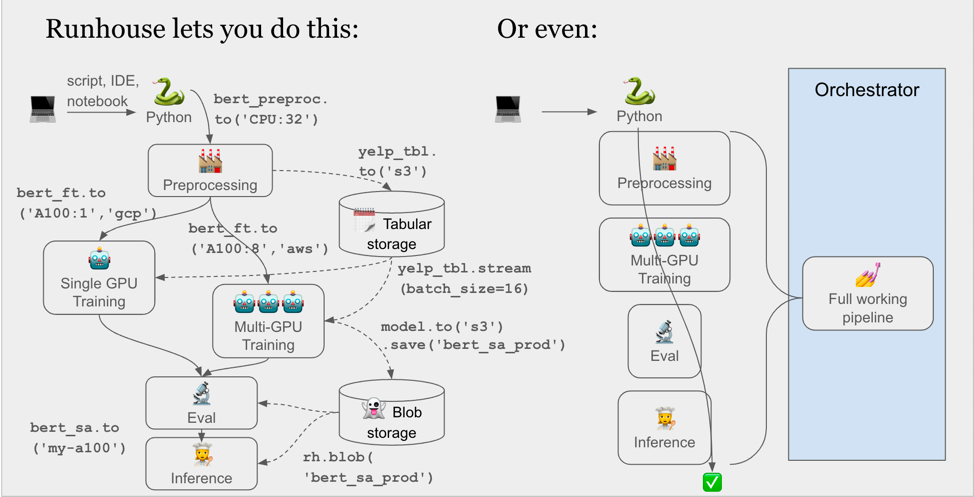
By way of a visual,
Take a look at this code (adapted from our first tutorial):
import runhouse as rh
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
def sd_generate(prompt):
model = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-base").to("cuda")
return model(prompt).images[0]
if __name__ == "__main__":
gpu = rh.cluster(name="my-a100", instance_type="A100:1", provider="cheapest")
sd_generate = rh.function(sd_generate).to(gpu, reqs=["./", "torch", "diffusers"])
sd_generate("An oil painting of Keanu Reeves eating a sandwich.").show()
sd_generate.save(name="sd_generate")By saving, I or anyone I share with can load and call into this service with a single line of code, from anywhere with a Python interpreter and internet connection (notebook, IDE, CI/CD, orchestrator node, etc.):
import runhouse as rh
sd_generate = rh.Function.from_name("sd_generate")
image = sd_generate("A hot dog made of matcha.")There's no magic yaml, DSL, code serialization, or "submitting for execution." We're just spinning up the cluster for you (or using an existing cluster), syncing over your code, starting a gRPC connection, and running your code on the cluster. Runhouse does things for you that you'd spend time doing yourself, in as obvious a way as possible.
On the data side, we can do things like:
# Send a folder up to a cluster (rsync)
rh.folder(path="./instance_images").to(system=gpu, path="dreambooth/instance_images")
gpu.run([f"accelerate launch diffusers/examples/dreambooth/train_dreambooth.py"
f"--instance_data_dir=dreambooth/instance_images "
f"--output_dir=dreambooth/output "])
# This goes directly cluster-> s3, doesn't bounce to local
outputs_s3 = rh.folder(system=gpu, path="dreambooth/outputs").to("s3", path="runhouse/dreambooth/outputs")
outputs_s3.save("dreambooth_outputs")To load down the folder in full later:
rh.Folder.from_name("dreambooth_outputs").to("here")We support interactive blob and table primitives too:
import runhouse as rh
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
def tokenize_dataset(dataset_table):
hf_dataset = dataset_table.to("here").convert_to("hf_dataset").fetch()
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("bert-base-cased")
tokenized_ds = hf_dataset.map(lambda x: tokenizer(x["text"], truncation=True, padding=True), batched=True)
return rh.table(tokenized_ds).write()
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Load a table in from anywhere (S3, GCS, Azure, cluster fs, local fs, etc)
raw_dataset = rh.table(system="gcs", path="my_bucket/my_data.parquet")
tokenize_dataset = rh.function(tokenize_dataset).to("^rh-32-cpu", env=["./", "transformers", "tokenizers"])
tokenized_table = tokenize_dataset(raw_dataset).to("gcs", path="my_bucket/preprocessed_data.parquet")
tokenized_table.save("preprocessed-dataset")And later:
import runhouse as rh
def train_model(preprocessed_table):
...
preprocessed_table.stream_format = "torch"
for batch in preprocessed_table.stream(batch_size=30):
...
return rh.blob(pickle.dumps(model)).write()
if __name__ == "__main__":
preprocessed_table = rh.Table.from_name("preprocessed-dataset")
train_model = rh.function(train_model).to("my-a100", env=["./", "torch", "transformers"])
trained_model = train_model(preprocessed_table)
trained_model.to("s3", path="runhouse/my_bucket").save(name="yelp_fine_tuned_bert")These APIs work from anywhere with a Python interpreter and an internet connection, so notebooks, scripts, pipeline nodes, etc. are all fair game. We currently support AWS, GCP, Azure, and Lambda Labs credentials through SkyPilot, as well as BYO cluster (just drop in an ip address and ssh key).
Runhouse is heavily under development and we expect to iterate on the APIs before reaching beta (version 0.1.0).
tldr;
pip install runhouse
# Or "runhouse[aws]", "runhouse[gcp]", "runhouse[azure]", "runhouse[all]"
sky check
# Optionally, for portability (e.g. Colab):
runhouse login
ray.init() in a Python interpreter. If you're
having trouble with this, let us know.
Runhouse can be installed with:
pip install runhouse
Depending on which cloud providers you plan to use, you can also install the following additional dependencies (to install the right versions of tools like boto, gsutil, etc.):
pip install "runhouse[aws]"
pip install "runhouse[gcp]"
pip install "runhouse[azure]"
# Or
pip install "runhouse[all]"
As this is an alpha, we push feature updates every few weeks as new microversions.
Runhouse supports both BYO cluster, where you interact with existing compute via their IP address and SSH key, and autoscaled clusters, where we spin up and down cloud instances in your own cloud account for you. If you only plan to use BYO clusters, you can disregard the following.
Runhouse uses SkyPilot for much of the heavy lifting with launching and terminating cloud instances. We love it and you should throw them a Github star ⭐️.
To verify that your cloud credentials are set up correctly for autoscaling, run
sky check
in your command line. This will confirm which cloud providers are ready to use, and will give detailed instructions if any setup is incomplete. SkyPilot also provides an excellent suite of CLI commands for basic instance management operations. There are a few that you'll be reaching for frequently when using Runhouse with autoscaling that you should familiarize yourself with, here.
Using Runhouse with only the OSS Python package is perfectly fine. However,
you can unlock some unique portability features by creating an (always free)
account on api.run.house and saving your secrets and/or
resource metadata there. For example, you can open a Google Colab, call runhouse login,
and all of your secrets or resources will be ready to use there with no additional setup.
Think of the OSS-package-only experience as akin to Microsoft Office,
while creating an account will make your cloud resources sharable and accessible
from anywhere like Google Docs. You
can see examples of this portability in the
Runhouse Tutorials.
To create an account, visit api.run.house,
or simply call runhouse login from the command line (or
rh.login() from Python).
Note: These portability features only ever store light metadata about your resources (e.g. my_folder_name -> [provider, bucket, path]) on our API servers. All the actual data and compute stays inside your own cloud account and never hits our servers. The Secrets service stores your secrets in Hashicorp Vault (an industry standard for secrets management), and our secrets APIs simply call Vault's APIs. We never store secrets on our API servers. We plan to add support for BYO secrets management shortly. Let us know if you need it and which system you use.
Tutorials can be found here. They have been structured to provide a comprehensive walkthrough of the APIs.
Docs can be found here. They include both high-level overviews of the architecture and detailed API references.
Check out Funhouse for running fun applications using Runhouse -- think the latest Stable Diffusion models, text generation models, launching Gradio spaces, and even more!
Please join our discord server here to message us, or email us (first name at run.house), or create an issue.
We welcome contributions! Please check out contributing if you're interested.