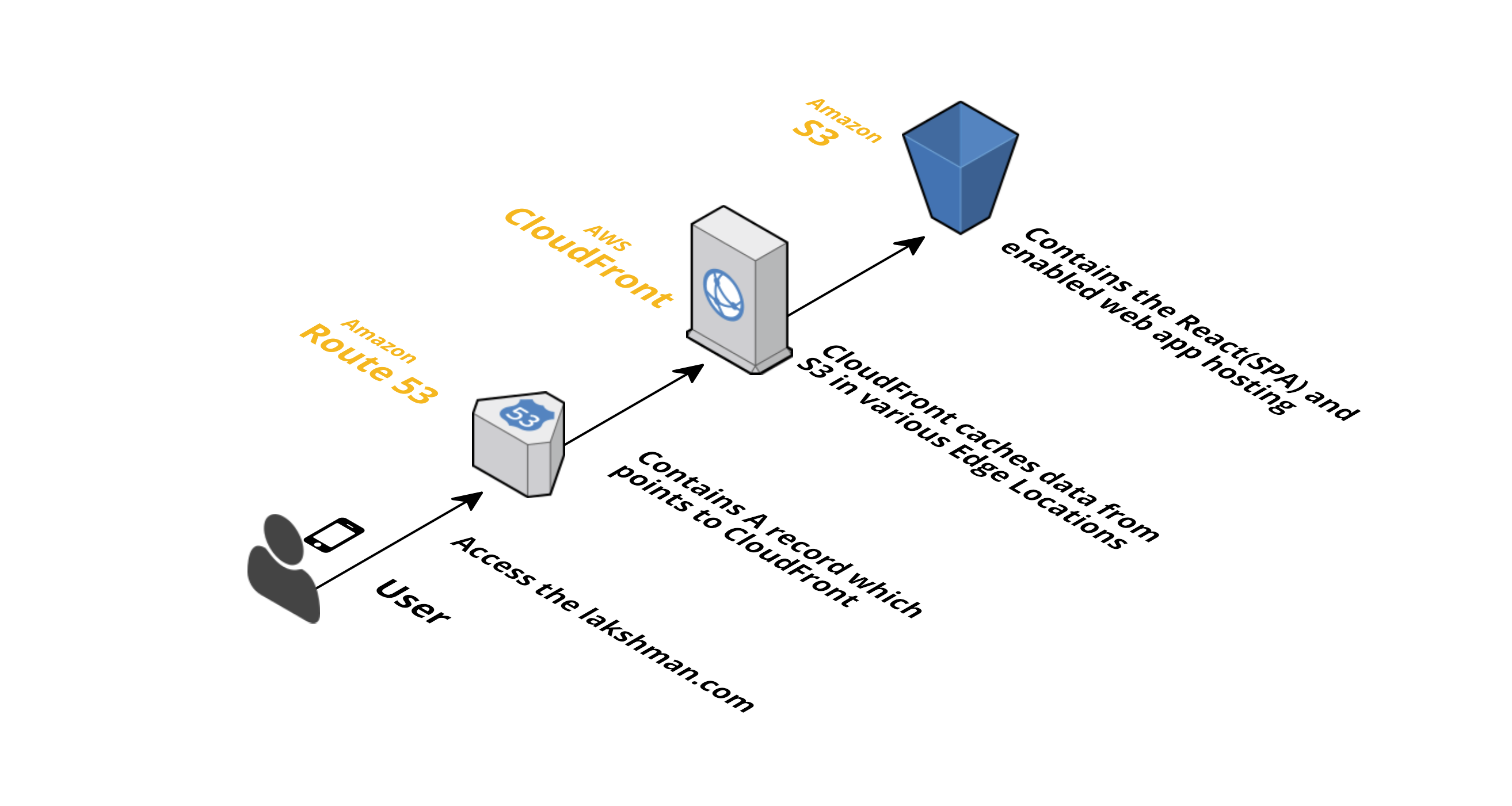
- This repo is aimed to list out the steps for setting up a Highly Available WebApp using Route53, CloudFront and S3.
- Listing out the best practices like the optimal TTL(time to live), gzip, SSL implementation, automating invalidation requests and so on.
Since setting up of each service requires a brief description, I have divided the instructions into three sections namely Hosting WebApp in S3, Caching using CloudFront and Routing using Route53. Each section contains the general steps, best practices and other miscellaneous things.
Amazon S3 is storage for the Internet. It has a simple web services interface that you can use to store and retrieve any amount of data, at any time, from anywhere on the web. It gives any developer access to the same highly scalable, reliable, fast, inexpensive data storage infrastructure that Amazon uses to run its own global network of web sites.
Amazon CloudFront is a global content delivery network (CDN) service that accelerates delivery of your websites, APIs, video content or other web assets. It integrates with other Amazon Web Services products to give developers and businesses an easy way to accelerate content to end users with no minimum usage commitments.
- Setting CF WebDistribution with S3.
- SSL for CloudFront Distribution.
- Gzip compression in CloudFront.
- TTL in CloudFront Distribution.
- Invalidating the CF cache and automating the same.
Amazon Route 53 is a highly available and scalable cloud Domain Name System (DNS) web service. It is designed to give developers and businesses an extremely reliable and cost effective way to route end users to Internet applications by translating names like www.example.com into the numeric IP addresses like 192.0.2.1 that computers use to connect to each other. Amazon Route 53 is fully compliant with IPv6 as well.
Custom mail domains are important. say, our domain is example.com, We need some emails like [email protected] and [email protected]. These can be created from the domain provider where you bought the domain.