Apache Cayenne is an open source persistence framework licensed under the Apache License, providing object-relational mapping (ORM) and remoting services.
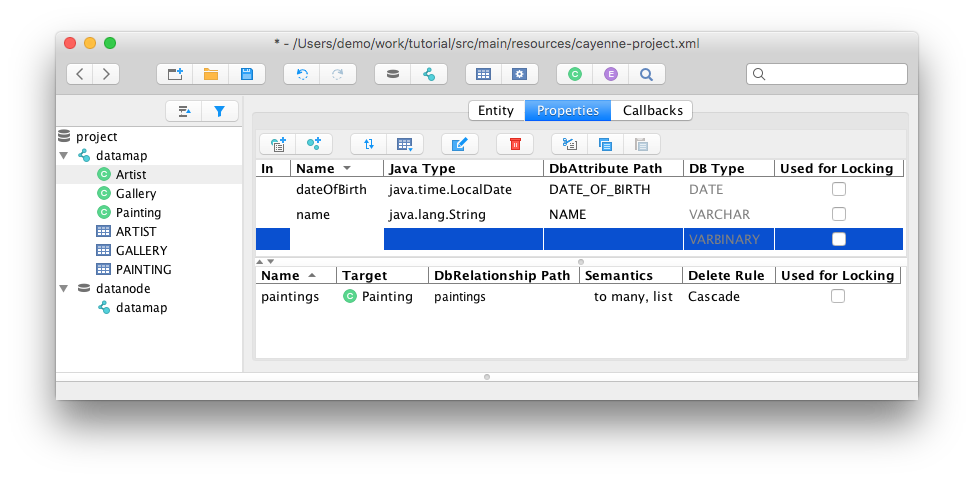
You can use Cayenne Modeler to manually create Cayenne project without DB. Binary distributions can be downloaded from https://cayenne.apache.org/download/
See tutorial https://cayenne.apache.org/docs/4.1/getting-started-guide/
Additionally you can use Cayenne Maven (or Gradle) plugin to create model based on existing DB structure. Here is example of Cayenne Maven plugin setup that will do it:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.cayenne.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>cayenne-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>4.1.M2</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>6.0.5</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<configuration>
<map>${project.basedir}/src/main/resources/demo.map.xml</map>
<cayenneProject>${project.basedir}/src/main/resources/cayenne-demo.xml</cayenneProject>
<dataSource>
<url>jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/cayenne_demo</url>
<driver>com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</driver>
<username>user</username>
<password>password</password>
</dataSource>
<dbImport>
<defaultPackage>org.apache.cayenne.demo.model</defaultPackage>
</dbImport>
</configuration>
</plugin>Run it:
mvn cayenne:cdbimport
mvn cayenne:cgenSee tutorial https://cayenne.apache.org/docs/4.1/getting-started-db-first/
And here is example of Cayenne Gradle plugin setup:
buildscript {
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
classpath group: 'org.apache.cayenne.plugins', name: 'cayenne-gradle-plugin', version: '4.1.M2'
classpath 'mysql:mysql-connector-java:6.0.5'
}
}
apply plugin: 'org.apache.cayenne'
cayenne.defaultDataMap 'demo.map.xml'
cdbimport {
cayenneProject 'cayenne-demo.xml'
dataSource {
driver 'com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver'
url 'jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/cayenne_demo'
username 'user'
password 'password'
}
dbImport {
defaultPackage = 'org.apache.cayenne.demo.model'
}
}
cgen.dependsOn cdbimport
compileJava.dependsOn cgenRun it:
gradlew build<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.cayenne</groupId>
<artifactId>cayenne-server</artifactId>
<version>4.1.M2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>compile group: 'org.apache.cayenne', name: 'cayenne-server', version: '4.1.M2'
// or, if Gradle plugin is used
compile cayenne.dependency('server')ServerRuntime cayenneRuntime = ServerRuntime.builder()
.addConfig("cayenne-demo.xml")
.build();ObjectContext context = cayenneRuntime.newContext();
Artist picasso = context.newObject(Artist.class);
picasso.setName("Pablo Picasso");
picasso.setDateOfBirth(LocalDate.of(1881, 10, 25));
Gallery metropolitan = context.newObject(Gallery.class);
metropolitan.setName("Metropolitan Museum of Art");
Painting girl = context.newObject(Painting.class);
girl.setName("Girl Reading at a Table");
Painting stein = context.newObject(Painting.class);
stein.setName("Gertrude Stein");
picasso.addToPaintings(girl);
picasso.addToPaintings(stein);
girl.setGallery(metropolitan);
stein.setGallery(metropolitan);
context.commitChanges();List<Painting> paintings = ObjectSelect.query(Painting.class)
.where(Painting.ARTIST.dot(Artist.DATE_OF_BIRTH).lt(LocalDate.of(1900, 1, 1)))
.prefetch(Painting.ARTIST.joint())
.select(context);// this is artificial property signaling that we want to get full object
Property<Artist> artistProperty = Property.createSelf(Artist.class);
List<Object[]> artistAndPaintingCount = ObjectSelect.columnQuery(Artist.class, artistProperty, Artist.PAINTING_ARRAY.count())
.where(Artist.ARTIST_NAME.like("a%"))
.having(Artist.PAINTING_ARRAY.count().lt(5L))
.orderBy(Artist.PAINTING_ARRAY.count().desc(), Artist.ARTIST_NAME.asc())
.select(context);
for(Object[] next : artistAndPaintingCount) {
Artist artist = (Artist)next[0];
long paintingsCount = (Long)next[1];
System.out.println(artist.getArtistName() + " has " + paintingsCount + " painting(s)");
}// Selecting objects
List<Painting> paintings = SQLSelect
.query(Painting.class, "SELECT * FROM PAINTING WHERE PAINTING_TITLE LIKE #bind($title)")
.params("title", "painting%")
.upperColumnNames()
.localCache()
.limit(100)
.select(context);
// Selecting scalar values
List<String> paintingNames = SQLSelect
.scalarQuery(String.class, "SELECT PAINTING_TITLE FROM PAINTING WHERE ESTIMATED_PRICE > #bind($price)")
.params("price", 100000)
.select(context);
// Insert values
int inserted = SQLExec
.query("INSERT INTO ARTIST (ARTIST_ID, ARTIST_NAME) VALUES (#bind($id), #bind($name))")
.paramsArray(55, "Picasso")
.update(context);https://cayenne.apache.org/docs/4.1/getting-started-guide/
https://cayenne.apache.org/docs/4.1/getting-started-db-first/
https://cayenne.apache.org/docs/4.1/cayenne-guide/
https://cayenne.apache.org/docs/4.1/api/
With a wealth of unique and powerful features, Cayenne can address a wide range of persistence needs. Cayenne seamlessly binds one or more database schemas directly to Java objects, managing atomic commit and rollbacks, SQL generation, joins, sequences, and more. With Cayenne's Remote Object Persistence, those Java objects can even be persisted out to clients via Web Services.
Cayenne is designed to be easy to use, without sacrificing flexibility or design. To that end, Cayenne supports database reverse engineering and generation, as well as a Velocity-based class generation engine. All of these functions can be controlled directly through the CayenneModeler, a fully functional GUI tool. No cryptic XML or annotation based configuration is required! An entire database schema can be mapped directly to Java objects within minutes, all from the comfort of the GUI-based CayenneModeler.
Cayenne supports numerous other features, including caching, a complete object query syntax, relationship pre-fetching, on-demand object and relationship faulting, object inheritance, database auto-detection, and generic persisted objects. Most importantly, Cayenne can scale up or down to virtually any project size. With a mature, 100% open source framework, an energetic user community, and a track record of solid performance in high-volume environments, Cayenne is an exceptional choice for persistence services.
Cayenne is available as free and open source under the Apache License, Version 2.0.