Please refer to the following for citation for further reading:
Wan, F., 2017, as_HybridNN: MNIST for Logical Learning with A Hybrid Neural Network, Github, https://github.com/as-wanfang/as_HybridNN, .
Wan, F., Song, C., 2017, Logical Learning Through a Hybrid Neural Network with Auxiliary Inputs, arXiv:1705.08200 [cs.AI], https://arxiv.org/abs/1705.08200.
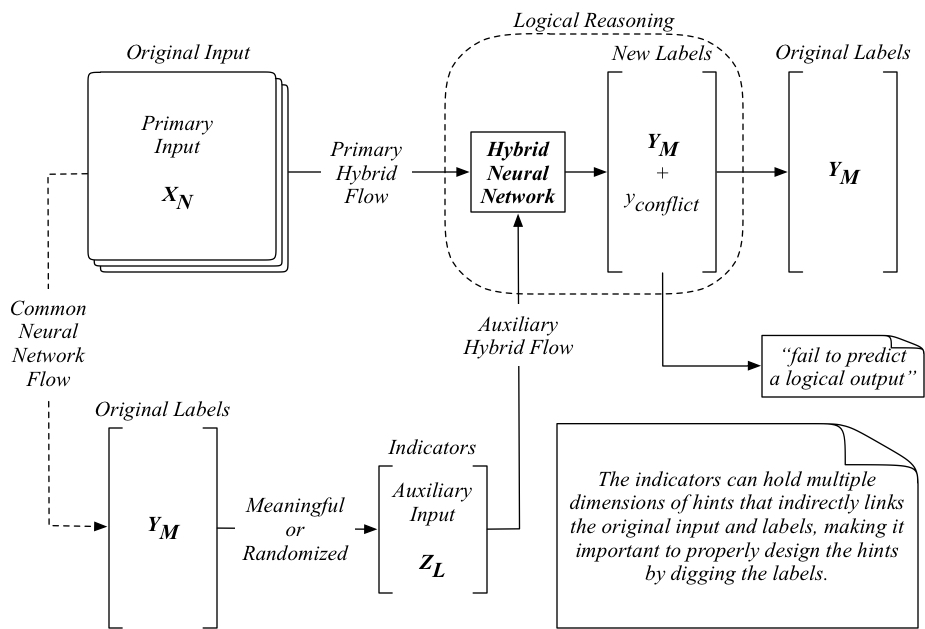
The Hybrid Neural Network (HybridNN) presented here intends to model a Logical Learning process by introducing an auxiliary input from the existing primary input or the original labels into the common Apparent Neural Networks (ApparentNN). To illustrate this process, the MNIST data is used in this repository as an example to demonstrate the design and use of such auxiliary indicators in a hybrid neural network.
The general structure of the HybrdNN is illustrated as below, where a set of Auxiliary Input is generated through digging the underneath knowledge buried in the label data. Such auxilary information is extracted as the indicators, a.k.a. the hints, to suggest a logical lable given a primary input. During the training process, the combinations of a primary input with all indicators are learned by the HybridNN as the logical knowledge. This process provides a logical learning of the knowledge in the data, including the apparent knowledge and the underneath logic.
When testing process of the HybridNN is also different from the ApparentNN, as illustrated below. A logical reasoning process is required to narrow down all answers computed to a logical one, which is a capability not available with the ApparentNN. One interesting fact is that we can design such logical reasoning in either a meaningful way or randomized one, which essentially enables one to model the unknown unknowns in the HybridNN.
The following set of indicators are designed to illustrate the design and use of the indicators, and their influence to logical learning.
| # | Meanings of the Indicators | Total Count | Size Distribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| 11 | Smaller than 5 or not | 2 | Equal / 5-5 |
| 12 | Even number or not | 2 | Equal / 5-5 |
| 13 | Prime number or not | 2 | Unequal / 5-5 |
| 14 | Zero or not | 2 | Unequal / 1-9 |
| 21 | None | 2 | Equal / 5-5 |
| 22 | None | 2 | Unequal / 3-7 |
| 23 | None | 5 | Equal / 2×5 |
| 24 | None | 10 | Equal / 1×10 |
| 31 | Multi-dimensional indicators | 4 | Equal / 5-5 |
| 32 | Reversed Prediction | 10 | Equal / 1-1 |
| 33 | Irrelevant Prediction | 2 | Equal / 1-1 |
The results are listed as below. Please note that the benchmarking MNIST prediction accuracy is at 98.91% produced by a CNN structure illustrated by Google. More details of the results are demonstrated using the codes in this repository.
| # | Logical Results | Logical Accuracy | Overall Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| 11 | 99.48% | 99.24% | 98.72% |
| 12 | 99.49% | 99.21% | 98.70% |
| 13 | 99.57% | 99.13% | 98.70% |
| 14 | 99.90% | 99.00% | 98.90% |
| 21 | 99.36% | 99.17% | 98.54% |
| 22 | 99.40% | 99.32% | 98.72% |
| 23 | 98.79% | 99.39% | 98.19% |
| 24 | 98.53% | 99.41% | 97.95% |
| 31 | 98.97% | 99.33% | 98.31% |
| 32 | 97.33% | 99.36% | 96.71% |
| 33 | 99.58% | 99.33% | 98.91% |
We proposed the concept of logical learning through a hybrid neural network with an additional auxiliary input, namely indicators, generated from the original labels, or even the original primary input data. Given the same data, the logical learning can always provide results with a higher logical accuracy that is supported by a logical reasoning process. We comprehensively introduced the concept of indicators for logical learning with the hybrid neural network on its design and use during model training as well as prediction. We also demonstrated the robustness of the proposed logical learning in a series of normal and special indicators. A few guidelines are summarized below to help assist the design and use of the indicators in a hybrid neural network.
- Any indicator is a good indicator for logical reasoning;
- Logical complexity positively relates to the confidence of an answer;
- Logical result is at the cost of overall accuracy;
- Meaningful indicators are not that good, and direct suggestions are not that bad;
- The design of the indicators is not limited by our understanding of the data.
This powerful tool provides us with a way to reflect the logical reasoning process while trying to comprehend more advanced concepts. It enables us to model the unknown unknowns structurally without the loss of confidence when a new and uncertain input is supplied. This process can be a meaningful one through the design of the indicators when we have established some prior understanding of the data, or a randomized one when we only care about a possible logic for a reasonable answer instead of the why behind.
The advancement of computing capabilities enables us to do brutal computation using neural networks for a most probable answer without caring much in the logic behind the answer. The average percentage of passing logical checks is at a relatively high level of 99.32%, leaving only a small fraction of data marked as illogical. However, this is mainly due to the high quality and simplicity of the MNIST data, which might not be the case for other machine learning tasks. It is particularly challenging when the cost of getting training data is expensive, especially when data collection requires physical interactions with the external environment, such as the robotics. When only a limited amount of data is available, it is essential to utilize all aspects of the data, including the logical reasoning, physical meaning, as well as environmental variables, etc., for a potential solution with the most probable confidence.
Future work requires a systematic research into the comprehensive and logical design of the indicators and hybrid neural network structures. The ongoing research of the as_DeepClaw and the as_urobotiq is an immediate direction to test further the application of the logical learning.