- Docs https://docs.redislabs.com/latest/rs/
- Provided by Redis - https://redis.com/redis-enterprise-software/overview/
- gcloud ssh working with
~/.ssh/google_compute_engineprivate key - with public key as
~/.ssh/google_compute_engine.pub - GCP IAM / service account exist, with
Compute AdminandDNS Administratorroles - GCP IAM service account exported
jsonin current folder - terraform
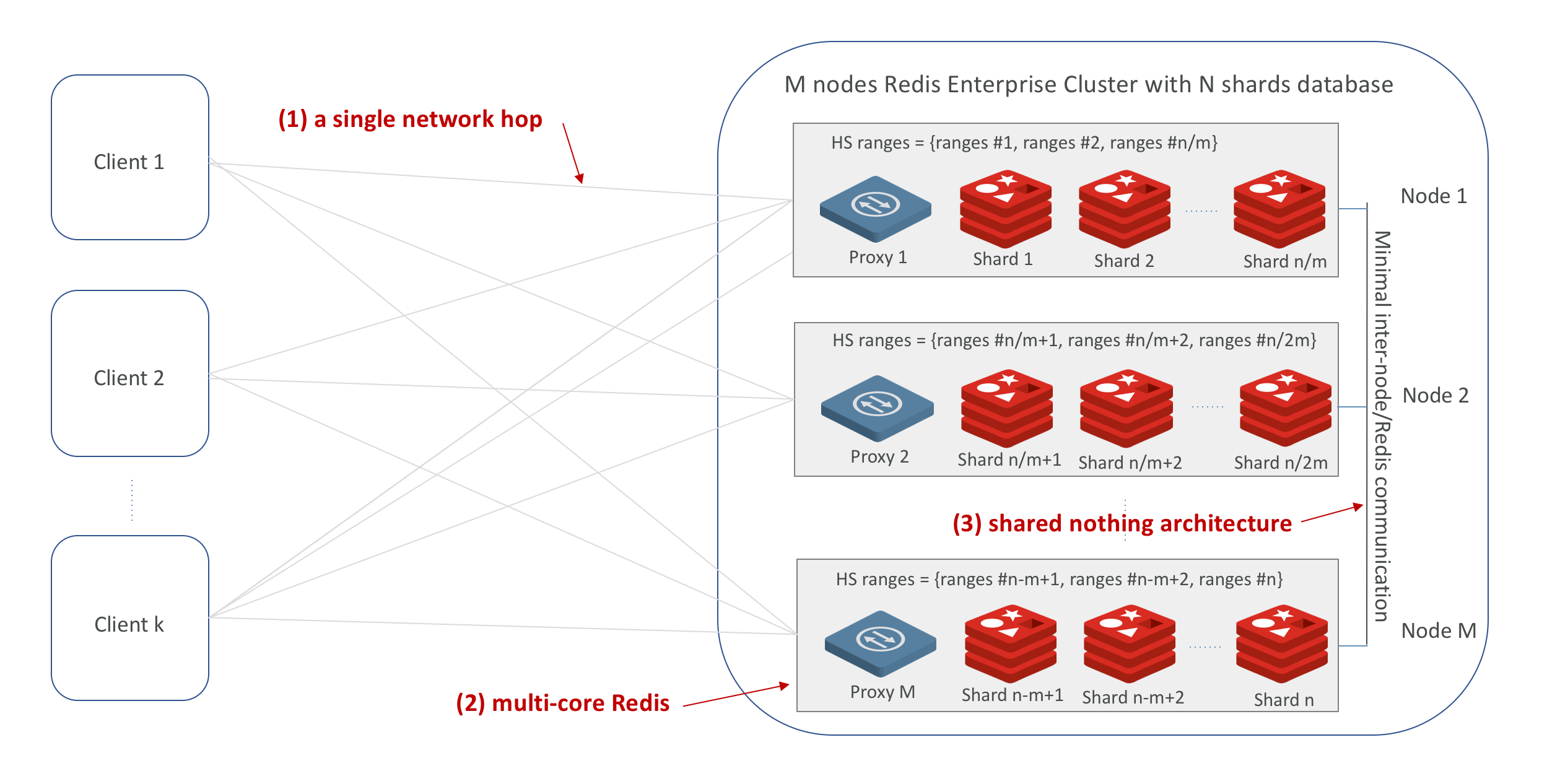
If using K8s GKE you will need
- roles
Kubernetes Engine Cluster AdminandService Account Admin(?) andService Account User(this can vary if you use create_service_account for your GKE/nodepool or use the project level user from the credential files)
Last used with: Terraform v1.7.5
terraform init- (optional) use a
terraform.tfvarsto override variable like those two important one or those that have no default:
yourname="testingthis"
credentials="GCP IAM key file.json"
- review
variable.tfto learn what you can override in yourterraform.tfvars- configure number of nodes and admin email
- review/change as needed
- configure the name of the json credentials file if needed
- configure the region (defaults europe-west1) and if needed the region zones (defaults ["b", "c", "d"]) (as defined by GCP for that region)
Here is an example file
yourname="..."
clustersize=1
machine_type = "e2-highmem-8" # 8 vCPU, 64 GB
# defaults to e2-standard-2 (2 vCPU, 8 GB)
## defaults to false
app_enabled = false
## defaults to false
gke_enabled = true
gke_clustersize = 3
gke_machine_type = "e2-standard-4"
# to delete use the cli as terraform destroy seems unreliable
# gcloud container node-pools delete redis-node-pool --cluster avasseur-dev-gke
Using multi-AZ zones, the cluster is made zone aware (aka rack-aware) for HA Redis database to be deployed in different zones.
terraform plan
terraform apply
will setup GCP, VPC, networks/firewall, DNS for Redis Enterprise
- node1 will be cluster master
- node2.. will be joining the cluster
- output will show Redis Enterprise cluster ui url and other info
- an admin password will be auto generated The nodes and cluster are created using external addr and DNS.
Example of a 2 nodes setup
Apply complete! Resources: 12 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
Outputs:
admin_password = "..."
admin_username = "[email protected]"
how_to_ssh = "gcloud compute ssh avasseur-dev-1"
how_to_ssh_to_app = "gcloud compute ssh avasseur-dev-app"
how_to_kubectl = "gcloud container clusters get-credentials avasseur-dev-gke"
nodes_dns = [
"node1.<yourname>.demo.redislabs.com.",
"node2.<yourname>.demo.redislabs.com.",
]
nodes_ip = [
"35.233.2.255",
"34.76.46.161",
]
rs_cluster_dns = "cluster.<yourname>.demo.redislabs.com"
rs_ui_dns = [
"https://node1.<yourname>.demo.redislabs.com:8443",
"https://cluster.<yourname>.demo.redislabs.com:8443",
]
rs_ui_ip = "https://35.233.2.255:8443"
terraform destroy
The Redis Enterprise node VM will be up but most likely the installation script will be running in background for cluster create and cluster join commands.
You should not try to setup the cluster manually using the Redis Enterprise web UI - but instead you can login using gcloud compute ssh ... and explore as user ubuntu for traces of the node installation:
ubuntu@avasseur-dev-1:~$ ls -al
total 56
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Apr 13 22:53 install
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 624 Apr 13 22:53 install.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 14532 Apr 13 22:53 install_rs.log
-rwxr--r-- 1 ubuntu root 129 Apr 13 22:53 node_externaladdr.sh
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2 Apr 13 22:53 node_index.terraform
If you stop the VM and need to restart them:
- you should restart the VM with GCP (Terraform will not do that for you)
- the startup-script will re-run, ignore RS as it is already installed, but update RS node external_addr if the IP changed Then:
- you must then use
terraform planand ``terraform apply` as you external IP addr may have changed. This will update them in the DNS (this may take time for DNS to propagate, ~5min). - in the meantime you can connect to node1 with the external_addr on https port 8443
Use gcloud with your machine node name that looks like:
gcloud compute ssh <yourname>-dev-1
You can explore logs in /home/ubuntu and in /var/log/syslog for the startup-script.
If you ssh into a node you can find installation logs:
sudo su - ubuntu
tail install.log
tail install_RS.log
and also use Redis Enterprise admin tools
rladmin
>status
CLUSTER NODES:
NODE:ID ROLE ADDRESS EXTERNAL_ADDRESS HOSTNAME SHARDS CORES FREE_RAM PROVISIONAL_RAM VERSION STATUS
*node:1 master 10.26.2.2 35.233.2.255 avatest-dev-1 0/100 2 6.27GB/7.77GB 4.87GB/6.38GB 6.0.12-58 OK
node:2 slave 10.26.2.3 34.76.46.161 avatest-dev-2 0/100 2 6.46GB/7.77GB 5.06GB/6.38GB 6.0.12-58 OK
see memtier.sh for a very basic example
It does assume password pass port 12000 and has my own DNS domain hardcoded so you may want to change the script for your own need.
You are best to run with app_enabled=true to spawn a client app machine and have memtier CLI already setup for you on the same colocated network & infrastructure.
With gke_enabled=true Terraform will create a GKE cluster and you can configure machines type and node pool machine count.
Currently the Redis Enterprise Kubernetes operator is not installed automatically. Check the product docs.
- if you stopped the VM in GCP, Terraform will assume their external IP are void and will clean up the DNS but will not restart the VM
https://github.com/radeksimko/terraform-examples/tree/master/google-consul
https://medium.com/slalom-technology/a-complete-gcp-environment-with-terraform-c087190366f0
https://gist.github.com/smford22/54aa5e96701430f1bb0ea6e1a502d23a