A C# Source Generator for obfuscating string or byte array values using multi-byte xor encryption.
Sample code:
using System;
using System.Buffers;
using System.Text;
using CompileTimeObfuscator;
namespace Sample;
internal static partial class Program
{
private static string PlainText() => "This is a plain string";
[ObfuscatedString("This is an obfuscated string 1")]
private static partial string ObfuscatedText1();
[ObfuscatedString("This is an obfuscated string 2")]
private static partial IMemoryOwner<char> ObfuscatedText2();
private static ReadOnlySpan<byte> PlainBytes() => "This is a plain bytes"u8;
[ObfuscatedBytes(new byte[] { (byte)'T', (byte)'h', (byte)'i', (byte)'s', (byte)' ', (byte)'i', (byte)'s', (byte)' ', (byte)'a', (byte)'n', (byte)' ', (byte)'o', (byte)'b', (byte)'f', (byte)'u', (byte)'s', (byte)'c', (byte)'a', (byte)'t', (byte)'e', (byte)'d', (byte)' ', (byte)'b', (byte)'y', (byte)'t', (byte)'e', (byte)'s', (byte)' ', (byte)'1', })]
private static partial byte[] ObfuscatedBytes1();
[ObfuscatedBytes(new byte[] { (byte)'T', (byte)'h', (byte)'i', (byte)'s', (byte)' ', (byte)'i', (byte)'s', (byte)' ', (byte)'a', (byte)'n', (byte)' ', (byte)'o', (byte)'b', (byte)'f', (byte)'u', (byte)'s', (byte)'c', (byte)'a', (byte)'t', (byte)'e', (byte)'d', (byte)' ', (byte)'b', (byte)'y', (byte)'t', (byte)'e', (byte)'s', (byte)' ', (byte)'2', })]
private static partial IMemoryOwner<byte> ObfuscatedBytes2();
private static void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine(PlainText());
Console.WriteLine(ObfuscatedText1());
using var memoryOwnerChar = ObfuscatedText2();
Console.WriteLine(memoryOwnerChar.Memory.Span.ToString());
Console.WriteLine(Encoding.UTF8.GetString(PlainBytes()));
Console.WriteLine(Encoding.UTF8.GetString(ObfuscatedBytes1()));
using var memoryOwnerByte = ObfuscatedBytes2();
Console.WriteLine(Encoding.UTF8.GetString(memoryOwnerByte.Memory.Span));
}
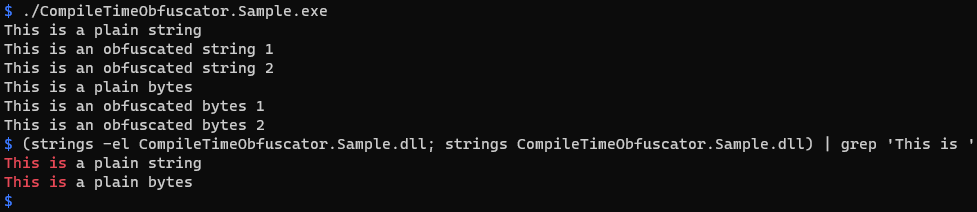
}The result of executing the sample code, and the result of strings command indicating that the obfuscation target string/bytes is not included in a binary as plain text:
- Visual Studio 2022 Version 17.3 or higher
- C# 9 or higher
- .NET Standard 2.1 or higher
I tested an operation in following environments:
- Visual Studio 2022 Version 17.5.1 and a project using C# 9 and .NET Core 3.1
- Visual Studio 2022 Version 17.5.1 and a project using C# 11 and .NET 6
- Add a nuget packege CompileTimeObfuscator.
- Use
CompileTimeObfuscator.ObfuscatedStringandCompileTimeObfuscator.ObfuscatedBytesin your source.
CompileTimeObfuscator.ObfuscatedStringcan obfuscate a string. The return type of the method can be astringorSystem.Buffers.IMemoryOwner<char>.CompileTimeObfuscator.ObfuscatedStringcan obfuscate a byte array. The return type of the method can be abyte[]orSystem.Buffers.IMemoryOwner<byte>.- For both attribute cases, I recommend using the
IMemoryOwner<T>version if execution efficiency is a priority.stringorbyte[]versions are wrappers onIMemoryOwner<T>version with additional conversion. - For both attribute cases, you can configure xor key length and whether the deobfuscated buffer is to be filled to zero when the
IMemoryOwner<T>.Disposemethod is called. To configure, add attribute arguments:
using CompileTimeObfuscator;
public partial class C
{
[ObfuscatedString("test", KeyLength = 1, ClearBufferWhenDispose = false)]
public static partial string M();
}The generator generates a following source after initialization:
// <auto-generated/>
#nullable enable
using System;
using System.Buffers;
using System.Diagnostics;
namespace CompileTimeObfuscator;
/// <summary>Obfuscate the specified string to preventing the string from appearing in a metadata. The obfuscated string is deobfuscated at runtime. The method must return <see cref="string"/> or <see cref="IMemoryOwner{T}"/> of type <see cref="char"/>.</summary>
[Conditional("COMPILE_TIME_ONLY")]
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Method, AllowMultiple = false, Inherited = false)]
internal sealed class ObfuscatedStringAttribute: Attribute
{
/// <summary>Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="ObfuscatedStringAttribute"/> with the specified string.</summary>
/// <param name="value">The string to obfuscate.</param>
internal ObfuscatedStringAttribute(string value)
{
}
/// <summary>Indicates the key length to obfuscate. A default value is 16.</summary>
public int KeyLength = 16;
/// <summary>Indicates whether a deobfuscated buffer will cleared after disposing an <see cref="IMemoryOwner{T}"/> object. A default value is true.</summary>
public bool ClearBufferWhenDispose = true;
}
/// <summary>Obfuscate the specified bytes to preventing the bytes from appearing in a metadata. The obfuscated bytes is deobfuscated at runtime. The method must return <see cref="byte"/>[] or <see cref="IMemoryOwner{T}"/> of type <see cref="byte"/>.</summary>
[Conditional("COMPILE_TIME_ONLY")]
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Method, AllowMultiple = false, Inherited = false)]
internal sealed class ObfuscatedBytesAttribute: Attribute
{
/// <summary>Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="ObfuscatedBytesAttribute"/> with the specified bytes.</summary>
/// <param name="value">The bytes to obfuscate.</param>
internal ObfuscatedBytesAttribute(byte[] value)
{
}
/// <summary>Indicates the key length to obfuscate. A default value is 16.</summary>
public int KeyLength = 16;
/// <summary>Indicates whether a deobfuscated buffer will cleared after disposing an <see cref="IMemoryOwner{T}"/> object. A default value is true.</summary>
public bool ClearBufferWhenDispose = true;
}
internal sealed class ClearableBuffer<T> : IMemoryOwner<T>
{
private T[]? _array;
private readonly int _length;
private readonly bool _clearBufferWhenDispose;
internal ClearableBuffer(int length, bool clearBufferWhenDispose)
{
_array = ArrayPool<T>.Shared.Rent(length);
_length = length;
_clearBufferWhenDispose = clearBufferWhenDispose;
}
public void Dispose()
{
if (_array is null) { return; }
// Even if clearArray parameter of ArrayPool<T>.Shared.Return is set to true,
// the array will not be cleared if the array is not returned to the pool.
// Therefore, clear the array manually here.
if (_clearBufferWhenDispose)
{
_array.AsSpan().Fill(default!);
}
ArrayPool<T>.Shared.Return(_array);
_array = null;
}
/// <summary>Returns <see cref="Memory{T}"/> that length is the originally required length. This behavior is different from an <see cref="IMemoryOwner{T}"/> returned from <see cref="MemoryPool{T}.Shared"/>.</summary>
public Memory<T> Memory
{
get
{
if (_array is null) { throw new ObjectDisposedException(GetType().FullName); }
return new Memory<T>(_array, 0, _length);
}
}
}For a following sample code:
using CompileTimeObfuscator;
public partial class C
{
[ObfuscatedString("test")]
public static partial string M1();
}A generator generates a following code, where key takes a different value for each generation:
// <auto-generated/>
#nullable enable
public partial class C {
public static partial string M1()
{
// The compiler optimize a code if `new byte[]{...}` is converted to ReadOnlySpan<byte>. https://vcsjones.dev/csharp-readonly-span-bytes-static/
System.ReadOnlySpan<byte> obfuscatedValue = new byte[]{117,226,34,33,148,30,41,116};
System.ReadOnlySpan<byte> key = new byte[]{1,226,71,33,231,30,93,116,226,66,50,253,253,60,3,216};
using var buffer = new CompileTimeObfuscator.ClearableBuffer<char>(obfuscatedValue.Length / 2, clearBufferWhenDispose: true);
var span = buffer.Memory.Span;
for (int i = span.Length - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
byte upper = (byte)(obfuscatedValue[2 * i + 1] ^ key[(2 * i + 1) % key.Length]);
byte lower = (byte)(obfuscatedValue[2 * i + 0] ^ key[(2 * i + 0) % key.Length]);
span[i] = (char)(upper << 8 | lower);
}
return new string(buffer.Memory.Span);
}
}The same is true when the return type is IMemoryOwner<char> or when obfuscating a byte array instead of a string:
using System.Buffers;
using CompileTimeObfuscator;
public partial class C
{
[ObfuscatedString("test")]
public static partial IMemoryOwner<char> M2();
[ObfuscatedBytes(new byte[] { (byte)'t', (byte)'e', (byte)'s', (byte)'t', })]
public static partial byte[] M3();
[ObfuscatedBytes(new byte[] { (byte)'t', (byte)'e', (byte)'s', (byte)'t', })]
public static partial IMemoryOwner<byte> M4();
}// omitted
public partial class C {
public static partial global::System.Buffers.IMemoryOwner<char> M2()
{
// omitted
System.ReadOnlySpan<byte> obfuscatedValue = new byte[]{92,228,183,152,126,175,18,190};
System.ReadOnlySpan<byte> key = new byte[]{40,228,210,152,13,175,102,190,199,226,250,53,66,54,118,164};
var buffer = new CompileTimeObfuscator.ClearableBuffer<char>(obfuscatedValue.Length / 2, clearBufferWhenDispose: true);
// omitted
return buffer;
}
}// omitted
public partial class C {
public static partial byte[] M3()
{
// omitted
System.ReadOnlySpan<byte> obfuscatedValue = new byte[]{26,241,65,188};
System.ReadOnlySpan<byte> key = new byte[]{110,148,50,200,144,242,236,138,214,152,182,90,190,251,180,67};
using var buffer = new CompileTimeObfuscator.ClearableBuffer<byte>(obfuscatedValue.Length, clearBufferWhenDispose: true);
// omitted
return buffer.Memory.ToArray();
}
}// omitted
public partial class C {
public static partial global::System.Buffers.IMemoryOwner<byte> M4()
{
// omitted
System.ReadOnlySpan<byte> obfuscatedValue = new byte[]{70,203,42,46};
System.ReadOnlySpan<byte> key = new byte[]{50,174,89,90,38,90,34,100,22,82,253,238,231,239,130,127};
var buffer = new CompileTimeObfuscator.ClearableBuffer<byte>(obfuscatedValue.Length, clearBufferWhenDispose: true);
// omitted
return buffer;
}
}Currently, a generator generates a source file for each method.
