SimulateBench: How Far Are We from Believable AI Agents? A Framework for Evaluating the Believability of Human Behavior Simulation
Human behavior simulation of AI agents necessitates the agents to possess a quality of believability, which is crucial as it facilitates users in establishing trust toward the agents and streamlines the fulfillment of the agents' goal. While recent advancements in Large Language Model (LLM) based agents have improved human behavior simulation, challenges inherent to LLMs (e.g., long context modeling) can undermine their believability. Consequently, evaluating AI agent believability becomes imperative. Unfortunately, prior research often neglects the negative impacts of LLM deficiencies. To address these gaps, we introduce two metrics for assessing LLM-based agent believability: consistency and robustness, together with a benchmark, SimulateBench, to evaluate the consistency and robustness of agents implemented with popular LLMs. We find that agents (i) struggle to accurately depict character information when presented with lengthy profile inputs; (ii) exhibit vulnerability to profile perturbations, and (iii) are significantly affected by certain key factors that impact their overall believability.
- The statistics of SimulateBench
- Profile Descriptive Framework & Character Dataset
- Consistency Dataset & Robustness Dataset
- Leaderboard
- Citation
| Statistical categories | number |
|---|---|
| Characters | 56 |
| Avg tokens per profile | 3277 |
| Avg tokens per question | 58 |
| Avg questions per character | # |
| Immutable Characteristic | 41 |
| Social Role | 52 |
| Relationship | 57 |
| Total benchmark questions | 8400 |
The Profile Descriptive Framework is introduced to document the information about a person comprehen- sively, consisting of three parts: Immutable Char- acteristic, Social Role, Relationship.
We selected characters from TV dramas of popular genres: The Simpsons (Animated), Friends (Comedy), Breaking Bad (Crime), and The Rings of Power(Science fiction). According to the profile descriptive framework, we extract the profile information from the fandom.
The profile is recorded in the json format for easy to use. You can find the profile of a character in the folder of "/db/profile/". The Social Role, Relationship information are stored in one json file.
for example, if you wann to load the profile of character of homer, his profile file are stored in
Immutable Chaacteristic: /db/profile/homer/profile_v1/basic_information.json
Social Role, Relationship: db/profile/homer/profile_v1/roles.json
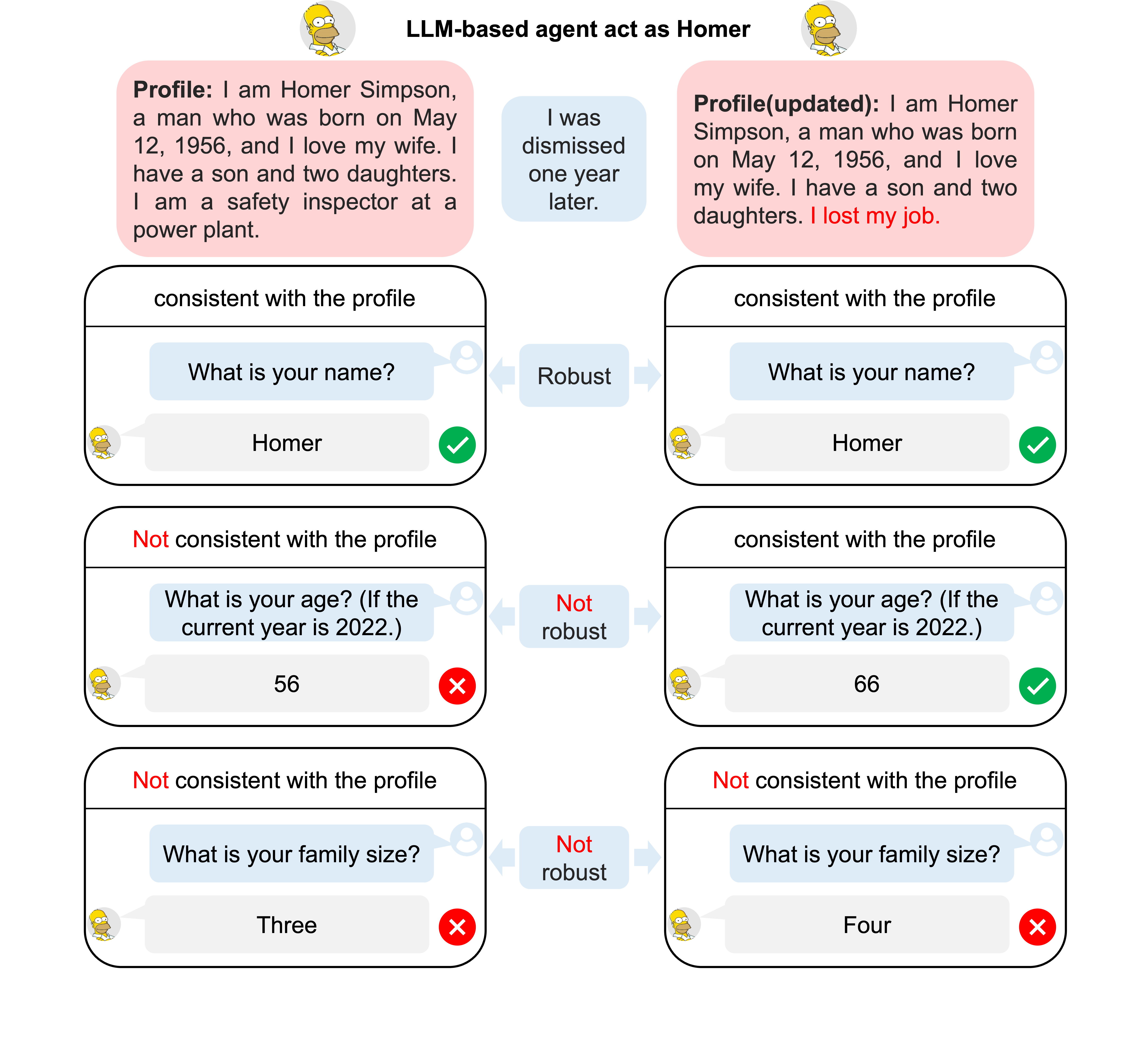
The two dataset is proposed to test the Consistency and robustness persormance of agents when prompted with the profile of a character to simulate the character. The two dataset is composed of single- choice questions and its gold answer. According to the profile descriptive framework, there are three kinds of questions related to Immutable Characteristics, Social Roles, and Relationships. For a character, you can find the dataset in the folder of "/db/benchmark_only_QA".
for example, if you wann to test the agent when simulating the character of homer, his dataset are stored in:
Immutable Chaacteristic: /db/benchmark_only_QA/basic_informationhomer/homer/questions.json
Social Role: /db/benchmark_only_QA/role_non_relation/homer/questions.json
Relationship: /db/benchmark_only_QA/role_relation/homer/questions.json
To test the agent's consistency ability, we will ask the agent to first simulate the character. Then, we will ask the agent to finsh the corresponding single-choice question in the Consistency Dataset. The accuracy score will be used as the measure of the consistency ability.
The Robustness Dataset is these datasets whose names are of the format of 'homer_{varients}'. To test agent's robustness ability, the agents is tested by compare their performance on the Consistency dataset and Robustness dataset. For example, if we want to test the agent's robustness ability when faced with age perturbations, we will first change the field of birthday year of homer in the profile, namely from 1956 to 1985. We then ask the agent to simulate homer(
/db/profile/homer/) and homer_1985(/db/profile/homer_1985/) by prompting the two profile to the agent respectively. Then, we will ask the agent to finish the test in the/db/benchmark_only_QA/{question_type}/homer/questions.jsonand/db/benchmark_only_QA/{question_type}/homer_1985/questions.jsonrespectively. Then, we can compare the two score on the two dataset to analyse the agent's robustness ability.
| Model | Score(CA) | Model Version | Model context size |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPT-4 | 0.93 | 0613 | 8k |
| GPT-3.5-turbo-16k | 0.74 | 0613 | 16k |
| Qwen-14B-Chat | 0.74 | 2023.09.25 | 8k |
| Qwen-7B-Chat | 0.70 | 2023.09.25 | 8k |
| Vicuna-13b-16k | 0.69 | v1.5 | 16k |
| ChatGLM2-6b-32k | 0.68 | 2023.07.31 | 32k |
| Longchat-7b-32k | 0.66 | v1.5 | 32k |
| XVERSE-13B-Chat | 0.64 | 2023.08.22 | 8k |
| ChatGLM2-6b | 0.63 | 2023.07.31 | 8k |
| Vicuna-7b-16k | 0.61 | v1.5 | 16k |
| Model | RCoV | Model Version | Model context size |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPT-4 | 1 | 0613 | 8k |
| GPT-3.5-turbo-16k | 3 | 0613 | 16k |
| Qwen-14B-Chat | 1 | 2023.09.25 | 8k |
| Qwen-7B-Chat | 2 | 2023.09.25 | 8k |
| Vicuna-13b-16k | 3 | v1.5 | 16k |
| ChatGLM2-6b-32k | 4 | 2023.07.31 | 32k |
| Longchat-7b-32k | 13 | v1.5 | 32k |
| XVERSE-13B-Chat | 1 | 2023.08.22 | 8k |
| ChatGLM2-6b | 4 | 2023.07.31 | 8k |
| Vicuna-7b-16k | 2 | v1.5 | 16k |
| Model | RCoV | Model Version | Model context size |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPT-4 | 2 | 0613 | 8k |
| GPT-3.5-turbo-16k | 5 | 0613 | 16k |
| Qwen-14B-Chat | 1 | 2023.09.25 | 8k |
| Qwen-7B-Chat | 2 | 2023.09.25 | 8k |
| Vicuna-13b-16k | 4 | v1.5 | 16k |
| ChatGLM2-6b-32k | 3 | 2023.07.31 | 32k |
| Longchat-7b-32k | 9 | v1.5 | 32k |
| XVERSE-13B-Chat | 2 | 2023.08.22 | 8k |
| ChatGLM2-6b | 5 | 2023.07.31 | 8k |
| Vicuna-7b-16k | 4 | v1.5 | 16k |
| Model | RCoV | Model Version | Model context size |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPT-4 | 2 | 0613 | 8k |
| GPT-3.5-turbo-16k | 4 | 0613 | 16k |
| Qwen-14B-Chat | 1 | 2023.09.25 | 8k |
| Qwen-7B-Chat | 2 | 2023.09.25 | 8k |
| Vicuna-13b-16k | 3 | v1.5 | 16k |
| ChatGLM2-6b-32k | 3 | 2023.07.31 | 32k |
| Longchat-7b-32k | 9 | v1.5 | 32k |
| XVERSE-13B-Chat | 2 | 2023.08.22 | 8k |
| ChatGLM2-6b | 4 | 2023.07.31 | 8k |
| Vicuna-7b-16k | 3 | v1.5 | 16k |
@article{xiao2023far,
title={How Far Are We from Believable AI Agents? A Framework for Evaluating the Believability of Human Behavior Simulation},
author={Xiao, Yang and Cheng, Yi and Fu, Jinlan and Wang, Jiashuo and Li, Wenjie and Liu, Pengfei},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2312.17115},
year={2023}
}