Code in this repository is aimed at using Google AI’s BERT model for sentiment classification. I suited some codes from the original BERT repository and then implement them on the Amazon review datasets.
This dataset originally consists of 4 million Amazon customer reviews and star ratings.
It contains 2 columns:
-
content: text content of the review.
-
label: the sentimental score of the review. “0” corresponds to 1- and 2-star reviews and “1” corresponds to 1- and 2-star. (3-star reviews i.e. reviews with neutral sentiment were not included in the original.)
This dataset was lifted from https://www.kaggle.com/bittlingmayer/amazonreviews but not in the format above, which is used in my processing, and here I only sample one tenth of them. The sample ratio of training set and validation set is 9:1.
-
Python 3.6
-
Tensorflow 1.12+
Add a new class based on the class DataProcessor to preprocess your datasets.
class AmazonProcessor(DataProcessor):
"""
Amazon Reviews data processor
"""
def _read_txt(self, data_dir, file_name):
with tf.gfile.Open(data_dir + file_name, "r") as f:
lines = []
for line in f:
lines.append(line.replace("\n", ""))
return lines
def get_train_examples(self, data_dir):
lines = self._read_txt(data_dir, "amazonTrain.txt")
examples = []
for (i, line) in enumerate(lines):
lineitems = line.split("\t")
guid = "Amazon Reviews train-%d" % (i)
text_a = tokenization.convert_to_unicode(lineitems[0])
label = tokenization.convert_to_unicode(lineitems[1])
examples.append(InputExample(guid=guid, text_a=text_a, label=label))
return examples
def get_dev_examples(self, data_dir):
lines = self._read_txt(data_dir, "amazonDev.txt")
examples = []
for (i, line) in enumerate(lines):
lineitems = line.split("\t")
guid = "Amazon Reviews dev-%d" % (i)
text_a = tokenization.convert_to_unicode(lineitems[0])
label = tokenization.convert_to_unicode(lineitems[1])
examples.append(InputExample(guid=guid, text_a=text_a, label=label))
return examples
def get_test_examples(self, data_dir):
lines = self._read_txt(data_dir, "amazonTest.txt")
examples = []
for (i, line) in enumerate(lines):
lineitems = line.split("\t")
guid = "Amazon Reviews test-%d" % (i)
text_a = tokenization.convert_to_unicode(lineitems[0])
label = tokenization.convert_to_unicode(lineitems[1])
examples.append(InputExample(guid=guid, text_a=text_a, label=label))
return examples
def get_labels(self):
return ["0", "1"]The original codes don't consider outputing metrics such as accuracy, loss and so on during the training phase and since the training curves are directions of adjusting parameters, we'd better to visualize those metrics.
Add more details to the output_spec of training phase :
if mode == tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN:
train_op = optimization.create_optimizer(
total_loss, learning_rate, num_train_steps, num_warmup_steps, use_tpu)
logging_hook = tf.train.LoggingTensorHook({"loss": total_loss}, every_n_iter=100)
output_spec = tf.contrib.tpu.TPUEstimatorSpec(
mode=mode,
loss=total_loss,
train_op=train_op,
training_hooks=[logging_hook],
scaffold_fn=scaffold_fn)We would be happier to have more evaluation results including Accuracy, Loss, Precision, Recall, AUC.
Add these metrics of validation phase by enriching the metric_fn function in evaluation mode:
def metric_fn(per_example_loss, label_ids, logits, is_real_example):
predictions = tf.argmax(logits, axis=-1, output_type=tf.int32)
accuracy = tf.metrics.accuracy(
labels=label_ids, predictions=predictions, weights=is_real_example)
auc = tf.metrics.auc(labels=label_ids, predictions=predictions, weights=is_real_example)
precision = tf.metrics.precision(labels=label_ids, predictions=predictions, weights=is_real_example)
recall = tf.metrics.recall(labels=label_ids, predictions=predictions, weights=is_real_example)
loss = tf.metrics.mean(values=per_example_loss, weights=is_real_example)
return {
"eval_accuracy": accuracy,
"eval_loss": loss,
"eval_auc": auc,
"eval_precision": precision,
"eval_recall": recall
}After adding details above, you can run the classification code for fine-tuning:
python run_classifier.py
--data_dir=../data/
--task_name=amazon
--vocab_file=../modelDependency/uncased_L-12_H-768_A-12/vocab.txt
--bert_config_file=../modelDependency/uncased_L-12_H-768_A-12/bert_config.json
--output_dir=../output/
--do_train=true
--do_eval=true
--init_checkpoint=../modelDependency/uncased_L-12_H-768_A-12/bert_model.ckpt
--max_seq_length=256
--train_batch_size=16
--learning_rate=5e-5
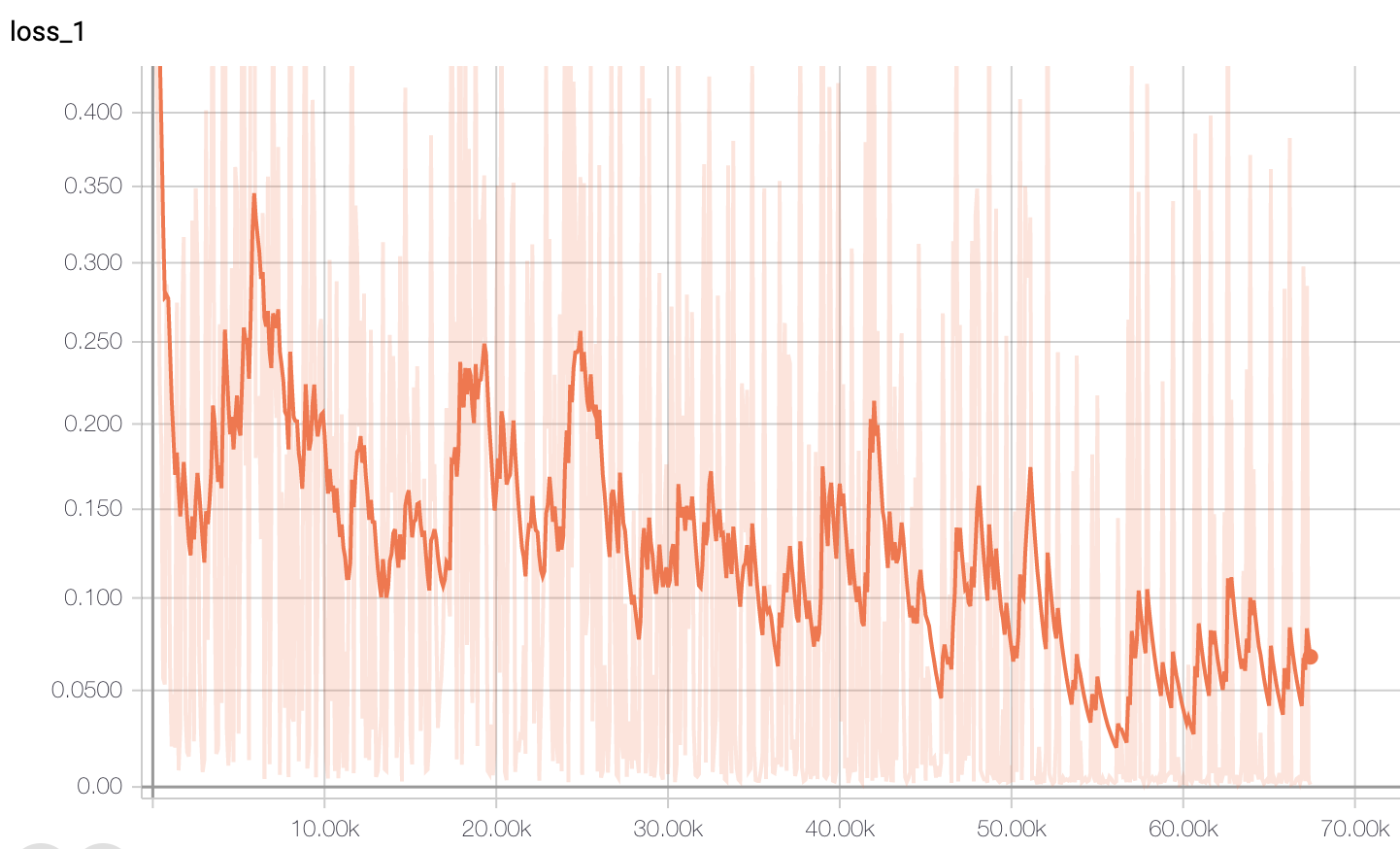
--num_train_epochs=3.0The loss curve while training is below, and we can see that it converge quickly at around step 10000.
Evalidation metrics on validation dataset:
***** Eval results *****
eval_accuracy = 0.963025
eval_auc = 0.9630265
eval_loss = 0.16626358
eval_precision = 0.9667019
eval_recall = 0.95911634
global_step = 67500
loss = 0.16626358
Wish you good hunting! ^ ^