forked from natverse/hemibrainr
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
/
README.Rmd
232 lines (163 loc) · 10.4 KB
/
README.Rmd
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
---
output:
md_document:
variant: markdown_github
---
<!-- README.md is generated from README.Rmd. Please edit that file -->
```{r, echo = FALSE}
knitr::opts_chunk$set(
collapse = TRUE,
comment = "#>",
fig.path = "README-"
)
```
<!-- badges: start -->
<img src="man/figures/logo.svg" align="right" height="139" />
[](https://travis-ci.org/natverse/hemibrainr)
[](https://codecov.io/gh/natverse/hemibrainr?branch=master)
[](https://www.tidyverse.org/lifecycle/#experimental)
<!-- badges: end -->
# hemibrainr
The goal of *hemibrainr* is to provide useful code for preprocessing and analysing data from the [Janelia FlyEM hemibrain](https://www.janelia.org/project-team/flyem) project. It makes use of the [natverse](https://github.com/natverse) R package, [neuprintr](https://github.com/natverse/neuprintr) to get hemibrain data from their connectome analysis and data hosting service [neuprint](https://github.com/connectome-neuprint/neuPrint). The dataset has been described [here]((https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.01.21.911859v1)). Using this R package in concert with the [natverse](https://github.com/natverse/natverse) ecosystem is highly recommended.
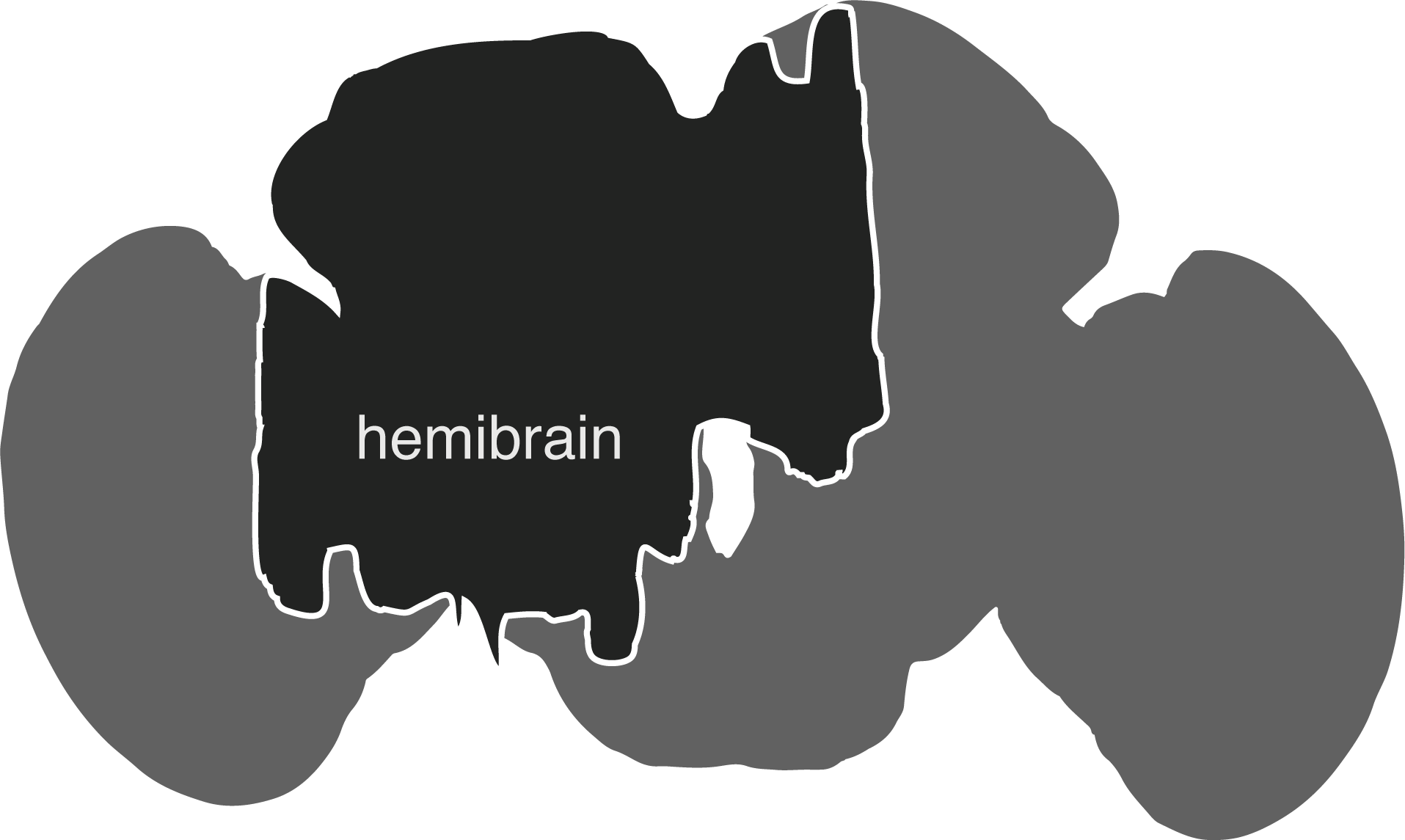
The hemibrain connectome comprises the region of the fly brain depicted below. It is ~21,662 ~full neurons, 9.5 million synapses and is about ~35% complete in this region:
<center>
</center>
## Get started with hemibrainr
### Installation
```{r install, eval = FALSE}
# install
if (!require("remotes")) install.packages("remotes")
remotes::install_github("natverse/hemibrainr")
# use
library(hemibrainr)
```
### Using hemibrainr
*hemibrainr* contains tools with which to quickly work with [hemibrain](https://neuprint.janelia.org/help/videos?dataset=hemibrain) and [FlyWire](https://ngl.flywire.ai/?local_id=c8c06ea181ad5447b04beacfc4cb1b66) neurons, and match up neurons within and between data sets.
If you can connect to the *hemibrainr* google shared drive, this package puts thousands of hemibrain and FlyWire neurons at your fingertips, as well as information on their compartments (e.g. axons versus dendrites), synapses and connectivity and between data set neuron-neuron matches. You can:
* Read thousands of pre-skeletonised FlyWire/hemibrain neurons from Google Drive
* Read FlyWire/hemibrain NBLASTs and NBLASTs to hemibrain neurons
* Read FlyWire/hemibrain neurons that are pre-transformed into a variety of brainspaces
Which is all useful stuff. You can explore our articles for more detailed information on what the package can do, and how to set it up with the data stored on Google drive - but can take a quick tour here:
```{r hemi, eval = FALSE}
# Load package
library(hemibrainr)
# Else, it wants to see it on the mounted team drive, here
options("Gdrive_hemibrain_data")
# We can load meta data for all neurons in hemibrain
db = hemibrain_neurons()
# And quickly read them from the drive, when we try to plot/analyse them!
hemibrain_view()
plot3d(hemibrain.surf, col = "grey", alpha = 0.1)
plot3d(db[1:10])
```
See which neurons have been matched up:
```{r see.matches, eval = FALSE}
# See matches, you can do this without hemibrain Google Team Drive access
View(hemibrain_matched)
# Get fresh matches, you cannot do this without access
## You will be prompted to log-in through your browser
hemibrain_matched_new <- hemibrain_matches()
## NOTE: includes hemibrain<->FlyWire matches!
```
### neuPrint authentication
In order to use *neuprintr*, which fetches data we want to use with *hemibrainr*, you will need to be able to login to a neuPrint server and be able to access it underlying Neo4j database.
You may need an authenticated accounted, or you may be able to register your `@gmail` address without an authentication process.
Navigate to a neuPrint website, e.g. https://neuprint.janelia.org, and hit 'login'. Sign in using an `@gmail` account.
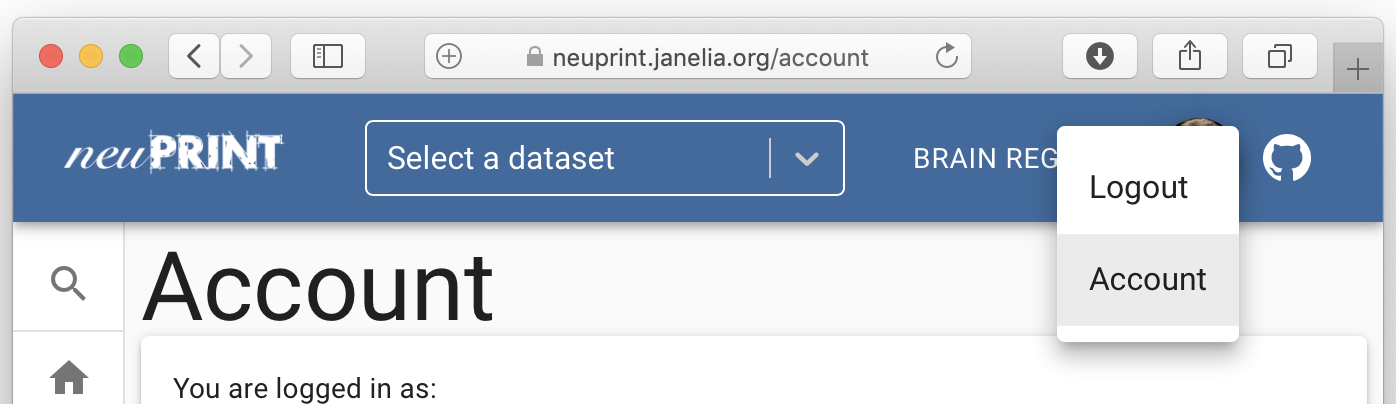
If you have authentication/the server is public, you will now be able to see your access token by going to 'Account':
To make life easier, you can then edit your `.Renviron` file to contain information about the neuPrint server you want to speak with, your token and the dataset hosted by that server, that you want to read. A convenient way to do this is to do
```{r, eval=FALSE}
usethis::edit_r_environ()
```
and then edit the file that pops up, adding a section like
```{r, eval=FALSE}
neuprint_server="https://neuprint.janelia.org"
# nb this token is a dummy
neuprint_token="asBatEsiOIJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJlbWFpbCI6ImIsImxldmVsIjoicmVhZHdyaXRlIiwiaW1hZ2UtdXJsIjoiaHR0cHM7Ly9saDQuZ29vZ2xldXNlcmNvbnRlbnQuY29tLy1QeFVrTFZtbHdmcy9BQUFBQUFBQUFBDD9BQUFBQUFBQUFBQS9BQ0hpM3JleFZMeEI4Nl9FT1asb0dyMnV0QjJBcFJSZlI6MTczMjc1MjU2HH0.jhh1nMDBPl5A1HYKcszXM518NZeAhZG9jKy3hzVOWEU"
```
Make sure you have a blank line at the end of your `.Renviron` file.
For further information try about neuprintr login, see the help for
`neuprint_login()`.
Finally you can also login on the command line once per session, like so:
```{r login2, eval = FALSE}
conn = neuprintr::neuprint_login(server= "https://neuprint.janelia.org/",
token= "asBatEsiOIJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJlbWFpbCI6ImIsImxldmVsIjoicmVhZHdyaXRlIiwiaW1hZ2UtdXJsIjoiaHR0cHM7Ly9saDQuZ29vZ2xldXNlcmNvbnRlbnQuY29tLy1QeFVrTFZtbHdmcy9BQUFBQUFBQUFBDD9BQUFBQUFBQUFBQS9BQ0hpM3JleFZMeEI4Nl9FT1asb0dyMnV0QjJBcFJSZlI6MTczMjc1MjU2HH0.jhh1nMDBPl5A1HYKcszXM518NZeAhZG9jKy3hzVOWEU")
```
This is also the approach that you would take if you were working with more than
two neuPrint servers.
### Connect to hemibrainr Google team drive
For this, you need access to th hemibrainr google team drive. Authentication is through an email account. Once you have access, there are two basic ways to mount the data for use:
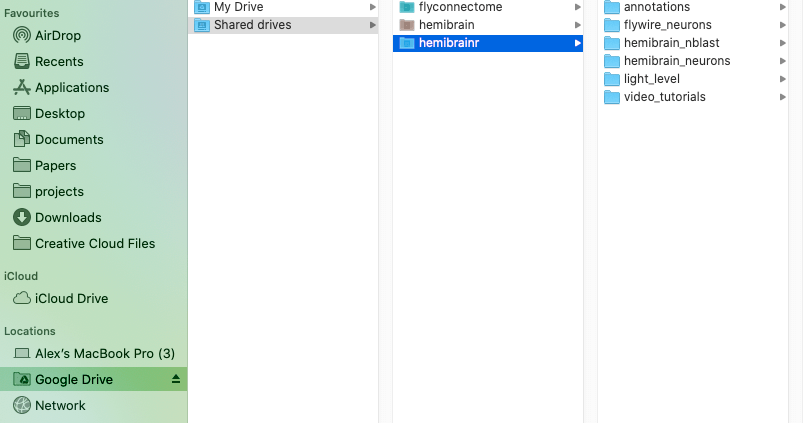
Option 1, mount your Google drives using [Google filestream](https://support.google.com/a/answer/7491144?hl=en). However, for this to work you will need [Google Workspace](https://workspace.google.com/pricing.html), Google's monthly subscription offering for businesses and organizations. One the [Google filestream](https://support.google.com/a/answer/7491144?hl=en) application is run, you should be able to see your drives mounted like external hard drive, as so:
<center>
</center>
Then, this should work:
```{r gdrive, eval = FALSE}
# Set a new Google drive, can be the team drive name or a path to the correct drive
hemibrainr_set_drive("hemibrainr") # No need to run this each time though, this is the default. Use if you want to use a different name drive.
# Now just get the name of your default team drive.
## This will be used to locate your team drive using the R package googledrive
hemibrainr_team_drive()
```
Option 2, this is free. You still need authenticated access to the hemibrainr Gogle team drive. It can then be mounted using [rclone](https://rclone.org/).
First, [download](https://rclone.org/downloads/) rclone for your operating system. You can also download from your system's command line (e.g. from terminal) and then configure it for the drive:
```{r rclone_download, engine = 'bash', eval = FALSE}
# unix/macosx
curl https://rclone.org/install.sh | sudo bash
rclone config
```
And now check this has worked:
```{r rclone_hemibrainr_mount, eval = FALSE}
# mounts in working directory
hemibrainr_rclone()
# Now hemibrain neurons are read from this mount
db = hemibrain_neurons() # read from the google drive
length(db)
plot3d(hemibrain_neurons[1:10])
# Specifically, from here
options("Gdrive_hemibrain_data")
# unmounts
hemibrainr_rclone_unmount()
# And now we are back to:
options("Gdrive_hemibrain_data")
```
For more detailed instructions, see [this article](https://natverse.github.io/hemibrainr/articles/google_filestream.html).
### Example: 'splitting' neurons
Let's get started with a useful function for splitting a neuron into its
axon and dendrite:
```{r example, eval = FALSE}
# Choose neurons
## These neurons are some 'tough' examples from the hemibrain:v1.0.1
### They will split differently depending on the parameters you use.
tough = c("5813056323", "579912201", "5813015982", "973765182", "885788485",
"915451074", "5813032740", "1006854683", "5813013913", "5813020138",
"853726809", "916828438", "5813078494", "420956527", "486116439",
"573329873", "5813010494", "5813040095", "514396940", "665747387",
"793702856", "451644891", "482002701", "391631218", "390948259",
"390948580", "452677169", "511262901", "422311625", "451987038"
)
# Get neurons
neurons = neuprint_read_neurons(tough)
# Now make sure the neurons have a soma marked
## Some hemibrain neurons do not, as the soma was chopped off
neurons.checked = hemibrain_skeleton_check(neurons, meshes = hemibrain.rois)
# Split neuron
## These are the recommended parameters for hemibrain neurons
neurons.flow = flow_centrality(neurons.checked, polypre = TRUE,
mode = "centrifugal",
split = "distance")
# Plot the split to check it
nat::nopen3d()
nlscan_split(neurons.flow, WithConnectors = TRUE)
```
## Tutorial
## Data
* HemiBrain (hemibrain:v1.0) : from ["A Connectome of the Adult Drosophila Central Brain"](https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.01.21.911859v1) (Xu, et al. 2020)
## Acknowledging the tools
neuPrint comprises a set of tools for loading and analyzing connectome data into a Neo4j database. Analyze and explore connectome data stored in Neo4j using the neuPrint ecosystem: [neuPrintHTTP](https://github.com/connectome-neuprint/neuPrintHTTP), [neuPrintExplorer](https://github.com/connectome-neuprint/neuPrintExplorer), [Python API](https://github.com/connectome-neuprint/neuprint-python).
This package was created by [Alexander Shakeel Bates](https://scholar.google.com/citations?user=BOVTiXIAAAAJ&hl=en) and [Gregory Jefferis](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gregory_Jefferis). You can cite this package as:
```{r citation, eval = FALSE}
citation(package = "hemibrainr")
```
**Bates AS, Jefferis GSXE** (2020). *hemibrainr: Code for working with data from Janelia FlyEM's hemibrain project.* **R package** version 0.1.0. https://github.com/natverse/hemibrainr