- Use mlpconv layers(small MLPs) instead of conventional convolutional layers to enhance discriminability for local patches within the receptive field.
- Use global average pooling instead of fully connected layers to do classification.
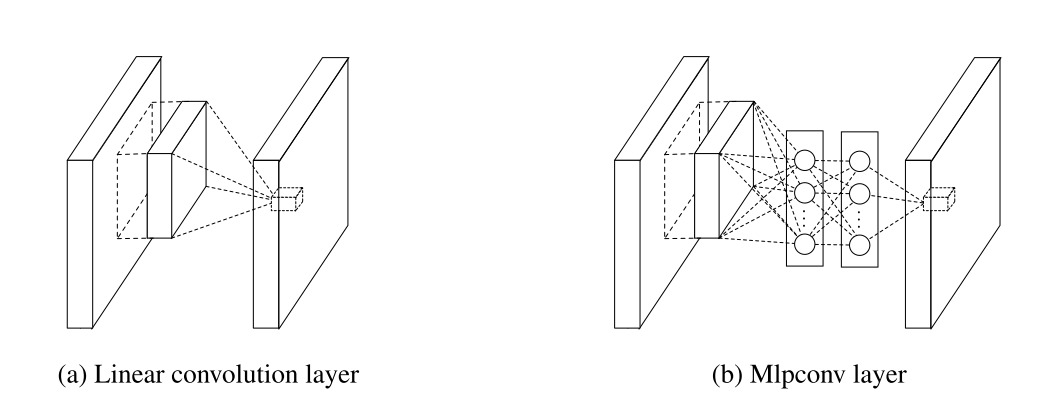 Note. From the point of implementation, MLPConv layer is just one convolutional layer plus one or many 1x1 convolutional layers. The Torch code below implements a building block of MLPConv layer.
Note. From the point of implementation, MLPConv layer is just one convolutional layer plus one or many 1x1 convolutional layers. The Torch code below implements a building block of MLPConv layer.
model:add(nn.SpatialConvolution(3,192,5,5,1,1,2,2))
model:add(nn.SpatialBatchNormalization(192,1e-3))
model:add(nn.ReLU(true))
model:add(nn.SpatialConvolution(192,160,1,1))
model:add(nn.SpatialBatchNormalization(160,1e-3))
model:add(nn.ReLU(true))
model:add(nn.SpatialConvolution(160,96,1,1))
model:add(nn.SpatialBatchNormalization(96,1e-3))
model:add(nn.ReLU(true))Benefits. Conventional convolutional layers are linear transformaions, while MLPConv slides small MLP over the feature map intervaned with non-linearity. So MLPConv has stronger capability to capture local abstraction. Thus avoids combination burden for the next layer.
Idea. Generate one feature map for each corresponding category of the classification task in the last mlpconv layer. Then take the average of each feature map, and the resulting vector is fed directly into the softmax layer. For instance, if one has 10 catagories, then the final MLPConv(or conventional convolution layer) outputs a 10 x M x M tensor, M is the sptail size of the feature maps. Then by averaging each MxM feature map, global average pooling gives a 10 dimension vector, which is then fed into a SoftMax layer to predict final classification result. Benifits:
-
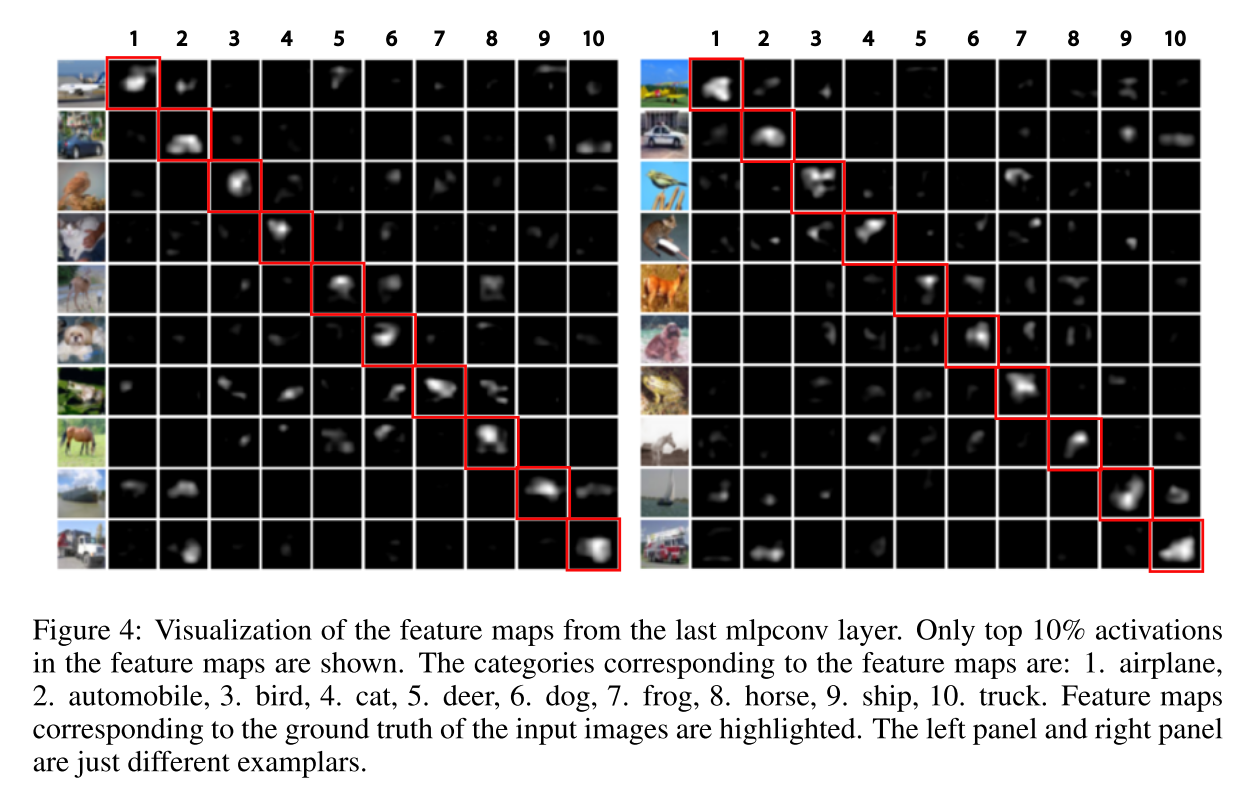
Global Average Pooling enforces correspondences between feature maps and categories so the classification process is more interpretable. For instance, in the picture below, within the 10 feature maps, the feature map corresponds to the ground truth category is most "fired" than other feature maps.

-
It has no parameters so it's more robust to overfit.
Lin, Min, Qiang Chen, and Shuicheng Yan. "Network in network." arXiv preprint arXiv:1312.4400 (2013).