A simple Vue3 wrapper for JSpreadsheet
modify jspreadsheet-ce's element and moving jsuites' dep into the bundle itself(&removing unused elements)
Updated when modelData changes array size (ex. push or pop array item), in both dimensions, the component doestn't update jspreadsheet instance data, now it will act accordingly. No need to manual refresh the component.
This is a major update. Instead of binding Vue's emit event to each event of JSpreadsheet, this commit uses jspreadsheet's global onevent to communicate changes between Vue modelValue and jspreadsheet instance, making the code less and working with more options such as jspreadsheet's sorting function.
Fixed Github Issue #2
Fixed a major problematic setting in package.json, which would cause webpack not to compile imported css from node_modules. For Node & webpack users, please must update to version ^0.2.5!
Obviously, you need to have your Vue3 properly configured.
npm install vue3_jspreadsheet...or with yarn
yarn add vue3_jspreadsheetImport js from unpkg.com:
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue3_jspreadsheet" />also requires to get the global css setting (from JSpreadsheet & JSuites).
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://unpkg.com/vue3_jspreadsheet/dist/vue3_jspreadsheet.css"/>You'll need to import global css first from the app's entry js file, as such:
import 'vue3_jspreadsheet/dist/vue3_jspreadsheet.css';then just import the component when you need it, for example:
<template>
<VueJSpreadsheet v-model="data" />
</template>
<script>
import VueJSpreadsheet from 'vue3_jspreadsheet';
import {ref} from 'vue';
export default {
components: {
VueJSpreadsheet
},
setup() {
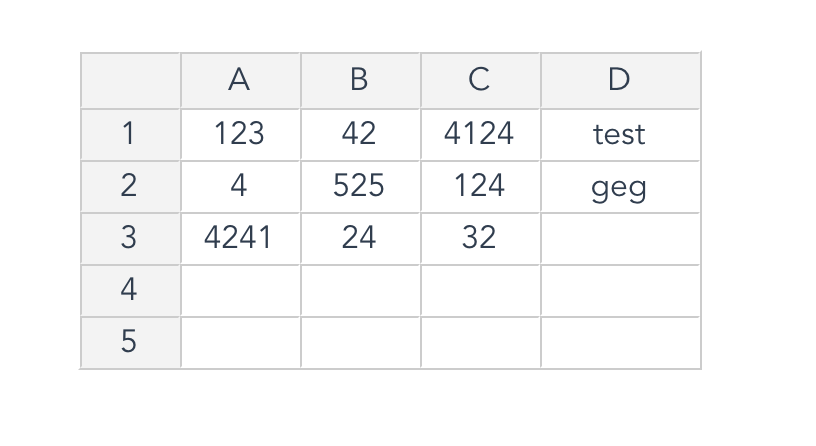
const data = ref([
[123,42,4124,"test"],
[4,525,124,"geg"],
[4241,"24",32]
]);
return {data};
},
}
</script>The result would look like this:
The component would be imported as global object named "VueJSpreadsheet", just register it with Vue. For example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1.0">
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue3_jspreadsheet"></script>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://unpkg.com/vue3_jspreadsheet/dist/vue3_jspreadsheet.css"/>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
</div>
<div id="app2">
</div>
<script>
// just mount it as the root component
var app = Vue.createApp(VueJSpreadsheet);
app.mount('#app');
// mount with component register
var app2 = Vue.createApp({
template: `
<VueJSpreadsheet v-model="test_data" />
`,
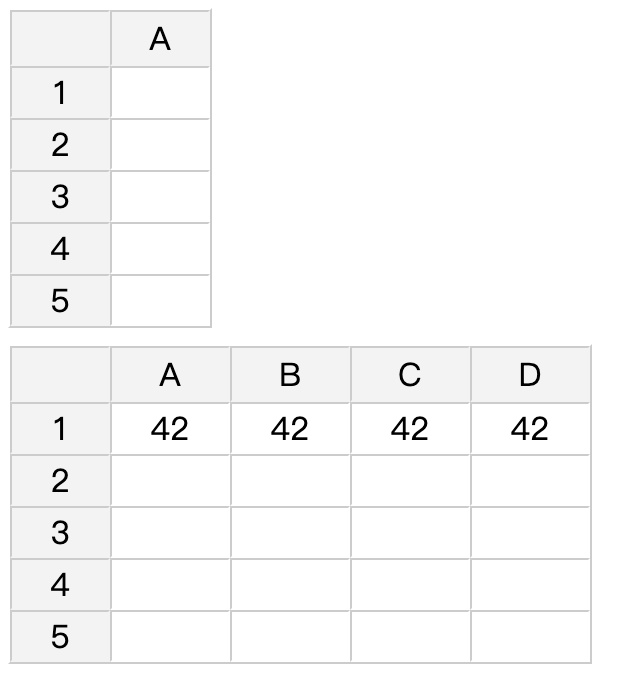
data(){
return {
test_data:[[42,42,42,42]]
}
},
});
app2.use(VueJSpreadsheet);
app2.mount('#app2');
</script>
</body>
</html>The result would look like this:
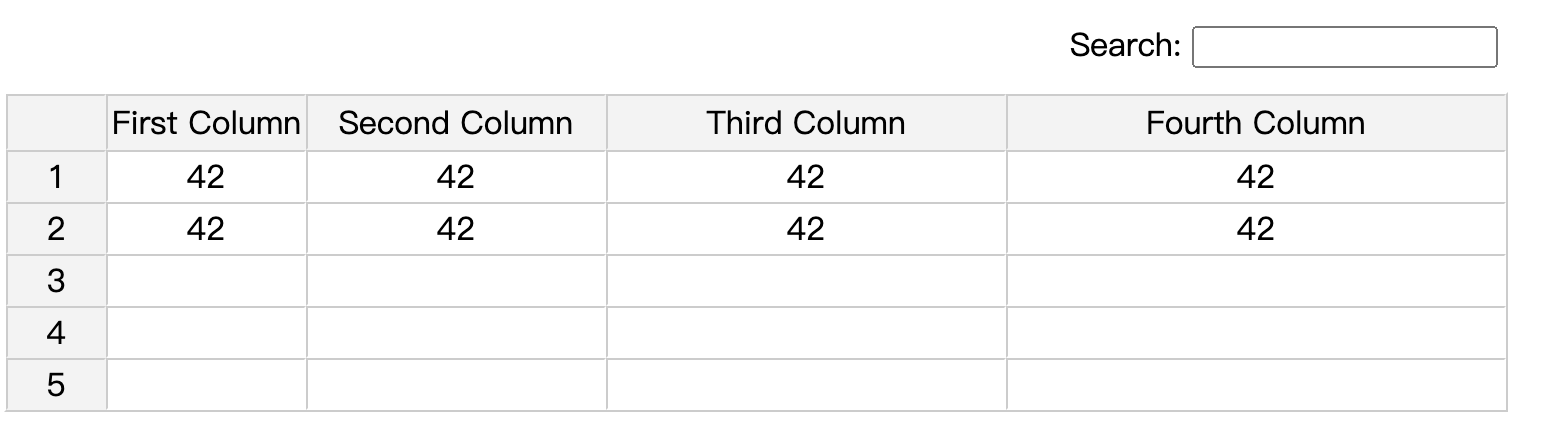
This component is quite simple. It just wrapps around the original JSpreadsheet. It has the v-model bind to the sheet's data, with bi-directional data flow.
Other custom options of JSpreadsheet are all avaliable via props:options.
Example setting:
<template>
<VueJSpreadsheet v-model="data" :options="myOption" />
</template>
<script>
import VueJSpreadsheet from "vue3_jspreadsheet";
import { ref } from "vue";
export default {
components: {
VueJSpreadsheet,
},
setup() {
const data = ref([
[42, 42, 42, 42],
[42, 42, 42, 42],
]);
const myOption = ref({
search: true,
columns: [
{ title: "First Column", width: 100 },
{ title: "Second Column", width: 150 },
{ title: "Third Column", width: 200 },
{ title: "Fourth Column", width: 250 },
],
});
return { data, myOption };
},
};
</script>