-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 3
/
README.Rmd
65 lines (43 loc) · 3.4 KB
/
README.Rmd
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
---
output:
md_document:
variant: gfm
---
<!-- README.md is generated from README.Rmd. Please edit that file -->
```{r, echo = FALSE}
knitr::opts_chunk$set(
collapse = TRUE,
comment = "#>",
fig.path = "README-"
)
```
# MIAmaxent
<!-- badges: start -->
[](https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=MIAmaxent)
[](https://cran.r-project.org/package=MIAmaxent)
<!-- badges: end -->
Read our [open-access paper](https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.5654) introducing MIAmaxent in *Ecology and Evolution*.
### Description
Tools for training, selecting, and evaluating maximum entropy (and standard logistic regression) distribution models. This package provides tools for user-controlled transformation of explanatory variables, selection of variables by nested model comparison, and flexible model evaluation and projection. It follows principles based on the maximum-likelihood interpretation of maximum entropy modeling (Halvorsen et al., 2015), and uses infinitely-weighted logistic regression for model fitting (Fithian & Hastie, 2013).
**MIAmaxent** is intended primarily for maximum entropy distribution modeling (Phillips et al., 2006; Phillips et al., 2017), and provides an alternative to the standard methodology for training, selecting, and using models. The major advantage in this alternative methodology is greater user control -- in variable transformations, in variable selection, and in model output. Comparisons also suggest that this methodology results in simpler models with equally good predictive ability, and reduces the risk of overfitting (Halvorsen et al., 2016).
The predecessor to this package is the MIA Toolbox, which is described in detail in Mazzoni et al. (2015).
### Installation
Install the release version from CRAN:
```{r, eval = FALSE}
install.packages("MIAmaxent")
```
Or the development version from GitHub:
```{r, eval = FALSE}
# install.packages(c("remotes", "R.rsp"))
remotes::install_github("julienvollering/MIAmaxent", build_vignettes = TRUE)
```
### User Workflow
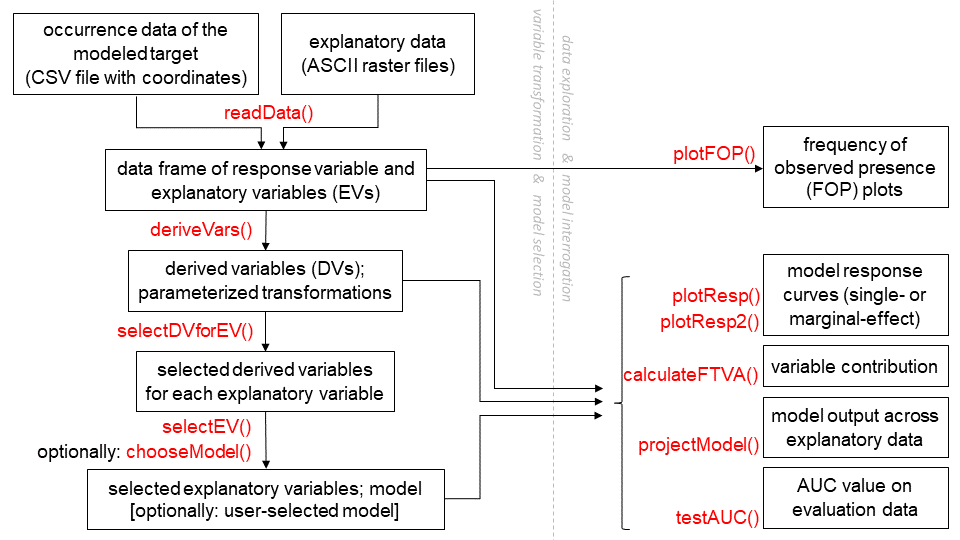
This diagram outlines a common workflow for users of this package. Functions are shown in red.
### References
Fithian, W., & Hastie, T. (2013). Finite-sample equivalence in statistical models for presence-only data. The annals of applied statistics, 7(4), 1917.
Halvorsen, R., Mazzoni, S., Bryn, A. & Bakkestuen, V. (2015) Opportunities for improved distribution modelling practice via a strict maximum likelihood interpretation of MaxEnt. Ecography, 38, 172-183.
Halvorsen, R., Mazzoni, S., Dirksen, J.W., Næsset, E., Gobakken, T. & Ohlson, M. (2016) How important are choice of model selection method and spatial autocorrelation of presence data for distribution modelling by MaxEnt? Ecological Modelling, 328, 108-118.
Mazzoni, S., Halvorsen, R. & Bakkestuen, V. (2015) MIAT: Modular R-wrappers for flexible implementation of MaxEnt distribution modelling. Ecological Informatics, 30, 215-221.
Phillips, S.J., Anderson, R.P., Dudík, M., Schapire, R.E., & Blair, M.E. (2017). Opening the black box: an open‐source release of Maxent. Ecography, 40(7), 887-893.
Phillips, S.J., Anderson, R.P. & Schapire, R.E. (2006) Maximum entropy modeling of species geographic distributions. Ecological Modelling, 190, 231-259.