In this section, all instrumentations are described, along with their purpose and the description of the data model produced.
Document load instrumentation produces spans about resources that have loaded by the time Window:load event fires. The root span generated is documentLoad. Following documentFetch and resourceFetch spans should have their parentId set as documentLoad.id.
If the page load request has a server-timing header present it is used to link documentFetch span to backend span via link tags. Page loads in Safari browsers are not linked with the backend trace, as server-timing API is not currently supported on Safari. Resources loading during page load are captured via performance.getEntriesByType(‘resource’) API.
Splunk Browser Agent supports capturing different resources, such as: script, link, css - font, iframe, XHR/fetch, img, favicon and manifest.json.Notice that if any of these resources has a server-timing header set in the response headers, such resources will also be linked to the APM trace.
Following tags are captured from the information captured by the documentLoad instrumentation:
| Name | Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
document.referrer |
string |
URI of the page that referred to this page via a href. |
"https://subdomain.example.com/" |
screen.xy |
string |
Width(x) and height(y) of the display. | "2560x1440" |
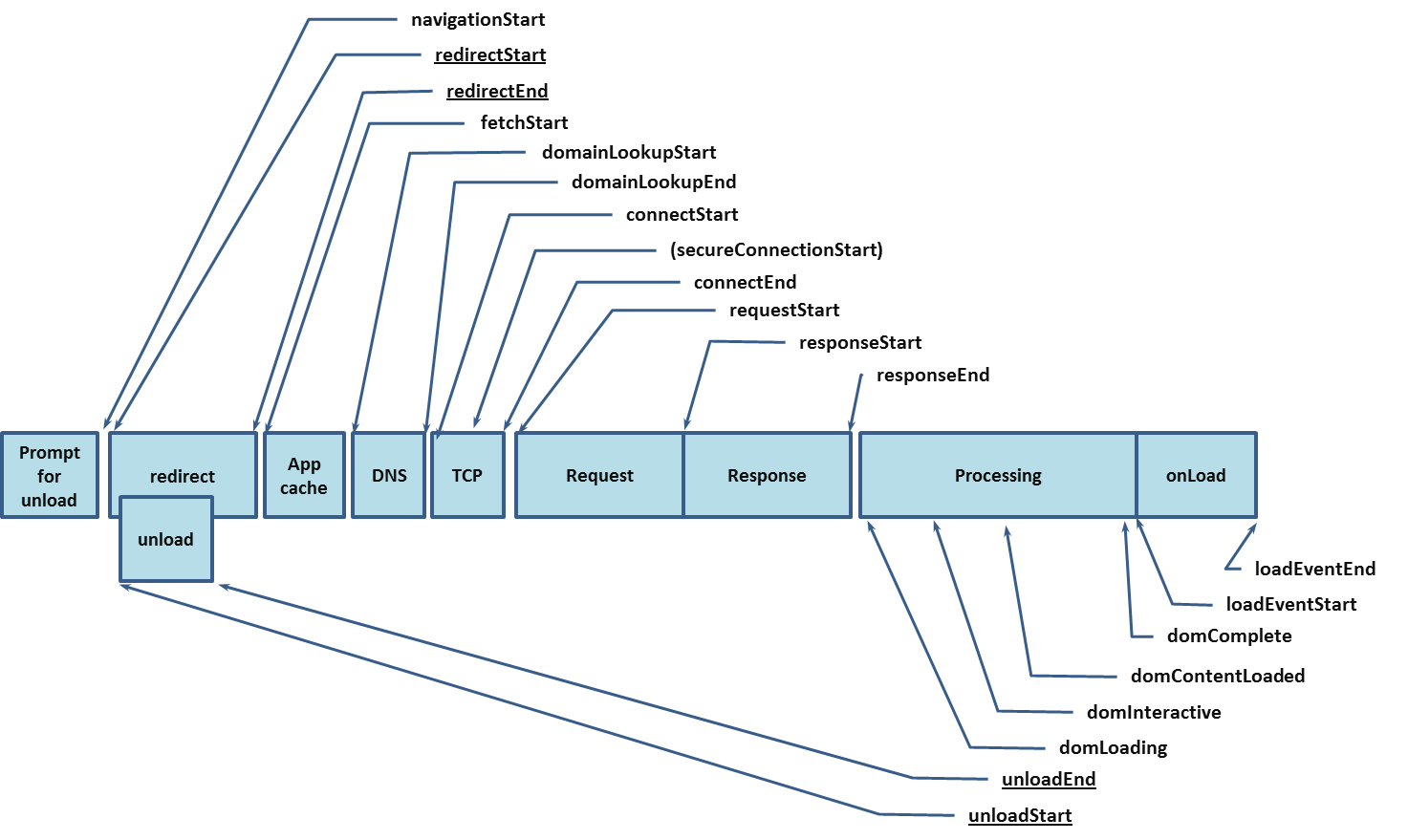
Following annotations are captured from the navigation timings, as specified by the W3C specification. The timestamps represent the NavigationTimings API events during a page load:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
fetchStart |
A timestamp immediately before the browser starts to fetch the resource. |
unloadEventStart |
A timestamp immediately before the user agent starts the unload event of the previous document. |
unloadEventEnd |
A timestamp immediately after the user agent finishes the unload event of the previous document. |
domInteractive |
A timestamp immediately before the user agent sets the current document readiness of the current document to interactive. |
domContentLoadedEventStart |
A timestamp representing the time value equal to the time immediately before the user agent fires the DOMContentLoaded event at the current document. |
domContentLoadedEventEnd |
A timestamp representing the time value equal to the time immediately after the current document's DOMContentLoaded event completes. |
domComplete |
A timestamp representing a time value equal to the time immediately before the browser sets the current document readiness of the current document to complete. |
loadEventStart |
A timestamp immediately before the load event of the current document is fired. |
loadEventEnd |
A timestamp when the load event of the current document is completed. |
Following tags are captured by instrumenting the documentFetch invocations:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
http.response_content_length |
number |
The size of the document received from the payload body as specified here. |
link.traceId |
string |
Trace identifier, captured from server-timing response header set by the APM agent |
link.spanId |
string |
Span identifier, captured from server-timing response header set by the APM agent |
The annotations captured by the documentFetch instrumentation are described in the HTTP request timing chapter.
Following tags are captured by instrumenting the resourceFetch invocations:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
http.response_content_length |
number |
The size of the document received from the payload body as specified here. |
http.url |
string |
URL of the requested resource. |
link.traceId |
string |
Trace identifier, captured from server-timing response header set by the APM agent |
link.spanId |
string |
Span identifier, captured from server-timing response header set by the APM agent |
The annotations captured by the resourceFetch instrumentation are described in the HTTP request timing chapter.
XHF/Fetch, as the name indicates, consists of two separate instrumentations. One is capturing Fetch API events and another for XMLHttpRequest events. The spans produced by the two instrumentations are almost identical. The only difference is set in the component tag value which differentiates between xml-http-request and fetch.
This instrumentation prepends the span name with HTTP + HTTP method name (eg. GET, POST). If the XHF/Fetch maps to a backend providing a server-timing header in the response, the link with the backend trace is also created by this instrumentation.
All the tags captured by the instrumentation and exposed in next table follow OpenTelemetry semantic conventions:
| Name | Type and Description |
|---|---|
http.method |
As specified in OpenTelemetry semantic conventions |
http.response_content_length |
As specified in OpenTelemetry semantic conventions |
http.host |
As specified in OpenTelemetry semantic conventions |
http.scheme |
As specified in OpenTelemetry semantic conventions |
http.status_code |
As specified in OpenTelemetry semantic conventions |
http.status_text |
As specified in OpenTelemetry semantic conventions |
http.user_agent |
As specified in OpenTelemetry semantic conventions |
http.url |
As specified in OpenTelemetry semantic conventions |
In addition, the XHR/Fetch instrumentation annotates the span with timestamps representing the time when the following XHR events fired:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
open |
number |
Time in UNIX epoch, measured in microseconds measured when XHR open event fires |
send |
number |
Time when XHR send event fires |
load |
number |
Time when XHR load event fires |
error |
number |
Time when XHR error event fires |
timeout |
number |
Time when XHR timeout event fires |
abort |
number |
Time when XHR abort event fires |
The annotations captured by the XHR/Fetch instrumentation are described in the HTTP request timing chapter.
Web Vitals instrumentation collects data about Google Web Vitals metrics. Web Vitals are captured as spans with zero duration. Every such span has a designated traceId and has no parent span.
Following tags are captured from the information captured by the webVitals instrumentation:
| Name | Web Vital | Description |
|---|---|---|
lcp |
Largest Contentful Paint | Measures loading performance by capturing the render time of the largest image or text block visible within the viewport. |
fid |
First Input Delay | Measures interactivity by capturing the timestamp between user interaction (i.e. click on a link, tap on a button, etc) to the time when the browser is actually able to begin processing event handlers in response to that interaction. |
cls |
Cumulative Layout Shift | Measures visual stability by capturing the sum of all individual layout shift scores for every unexpected layout shift that occurs during the entire lifespan of the page. A layout shift occurs any time a visible element changes its position from one rendered frame to the next. |
This instrumentation collects data about resources loading after a page load event. By default, the instrumentation enables instrumenting for resource types <script>and <img> but adjusting the configuration allows it to harvest additional telemetry, given that the resource supports PerformanceResourceTiming interface.
Common use case where capturing information via this information is for example loading more images on scroll events.
The spans captured by this instrumentation would match the data model described in the resourceFetch section.
This instrumentation collects information on the user's activity with elements that have a registered event listener using Element.addEventListener. Events captured by this listener generate a span with the name matching the DOM event name.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
event_type |
string |
Event name (e.g. click). |
target_element |
string |
Name of the target element (e.g. BUTTON). |
target_xpath |
string |
XPath of the target element. |
Following is an example listener which would be instrumented with this instrumentation:
<button id="add_row">Add a row</button>
document.getElementById('add_row').addEventListener('click', function (event) {
fetch('/api/row', {method: 'PUT'});
});User interaction instrumentation also instruments History API in order to provide visibility into the browser's session history. The history API is used to track URL changes that do not reload the page and is used in single page applications. Instrumentation also tracks URL changes done via changing the location.hash (by listening to hashchange event). Route change has no duration; it is just an event letting you know that the change happened. The info is sent as routeChange span with following tags:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
component |
string |
"user-interaction" |
prev.href |
string |
Page URL before the route change. |
location.href |
string |
Page URL after the route change. |
This instrumentation collects information about long tasks. For every long task a span is created.
Span attributes include containers that the task occurred within. For tasks that don't occur within the top level page, the containerId, containerName and containerSrc fields provide information about the source of the task.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
longtask.name |
string |
Usually self, see specification for all possible values. |
longtask.entry_type |
number |
Always set to longtask |
longtask.duration |
number |
Duration of the task. |
attribution.name |
string |
See TaskAttributionTiming |
attribution.entry_type |
string |
See TaskAttributionTiming |
attribution.start_time |
number |
See TaskAttributionTiming |
attribution.duration |
number |
See TaskAttributionTiming |
attribution.container_type |
string |
See TaskAttributionTiming |
attribution.container_src |
string |
See TaskAttributionTiming |
attribution.container_id |
string |
See TaskAttributionTiming |
attribution.container_name |
string |
See TaskAttributionTiming |
The instrumentation doesn’t change the raw data captured from API’s, so for a more detailed description about the attributes see PerformanceLongTaskTiming and TaskAttributionTiming interfaces.
This instrumentation captures websocket lifecycle events and populates span with the information captured by the information. Websocket instrumentation is disabled by default. The instrumentation is disabled, as without the understanding about the purpose and design of the communication protocol it would likely not be capturing useful information from the native websocket. This can be enabled in configuration.
The instrumentation is capturing spans from websocket connect, send and onmessage events.
Captures information from connect event.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
http.url |
string |
Websocket URL. |
duration |
number |
Time between websocket constructor call and ws.open event firing. |
protocols |
string | array |
Protocols passed to the websocket constructor. |
error |
string |
true / false depending if an error occurred. Errors are captured during websocket construction(eg. Incorrect url) or when ws.error event fires. |
error.message |
string |
Websocket error event message. |
Captures information from send and onmessage events.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
http.url |
string |
Websocket URL. |
response_content_length |
number |
Payload size in bytes. |