Note: This repository is no longer actively maintained.
Please visit our new repository for the latest updates and improvements: github.com/farm-ng/amiga-ros-bridge
If you have any questions or need assistance, feel free to contact us at discourse.farm-ng.com/.
This repository contains a ROS bridge for the Farm-ng Amiga platform written in Rust.
Disclaimer: the Amiga stack does not leverage ROS for control, but rather uses a gRPC service for control. This bridge is provided as a convenience for users who wish to use ROS for control. For performance critical applications, we recommend using the gRPC service directly.
The ROS bridge, currently supported for ROS Noetic, interfaces with the Amiga gRPC services for control with ROS Twist messages.
Using the ROS bridge with the amiga requires an Amiga OS >= v1.2.0.
The ROS bridge allows you to publish Twist commands on the /amiga/cmd_vel topic to drive the Amiga and subscribe to TwistStamped measured rates on the /amiga/vel topic.
There are currently 3 methods for using the amiga_ros_bridge:
- Running the
amiga_ros_bridge(and ROS master) on the Amiga, with other ROS nodes on your PC connected to the Amiga ROS master- Look for sections tagged as
[Method 1]
- Look for sections tagged as
- Running the
amiga_ros_bridge(and ROS master) on your PC, connected to the Amiga canbus service over gRPC- Look for sections tagged as
[Method 2]
- Look for sections tagged as
- Running the
amiga_ros_bridge(and ROS master) on your PC, using the mock server- Look for sections tagged as
[Method 3]
- Look for sections tagged as
-
Control
- Subscribed to by ROS bridge
- Topic:
/amiga/cmd_vel - Format:
geometry_msgs/Twist
-
Measured
- Published by ROS bridge
- Topic:
/amiga/vel - Format:
geometry_msgs/TwistStamped
For: [Method 1]
If you would like run the amiga_ros_bridge on the Amiga,
you will need to gain access to the ROS bridge docker container.
Please contact [email protected] for instructions and credentials.
For: [Method 2], [Method 3]
To run the amiga_ros_bridge on your PC, you will need:
- ROS Noetic install instructions
- Rust install instructions.
- Rust is only needed if you will run the
amiga_ros_bridgeor any Rust examples on your PC.
- Rust is only needed if you will run the
NOTE: Using ROS on your PC means you're either running some flavor of Linux or know how to run ROS in a VM on your other OS.
For: [Method 1], [Method 2], [Method 3]
We hope to soon package a pre-compiled
amiga_ros_bridgein the ros bridge docker container installed on your Amiga for running with[Method 1]. In the meantime, you will need to manually install theamiga_ros_bridgeas you would on your PC.
Create a catkin workspace, if you don't already have one, following the instructions at ROS Tutorials - create_a_workspace. If this is a new project, it is recommended to create a new, separate catkin workspace.
The remaining instructions will assume you're using a catkin ws at
~/catkin_ws.
Clone the repository and initialize the farm-ng-amiga submodule.
cd ~/catkin_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/farm-ng/amiga-ros-bridge.git
cd amiga-ros-bridge
git submodule update --init
cd ~/catkin_wsGo to your ROS workspace and source the setup.bash file:
cd ~/catkin_ws
source ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bashWarning: this may take ~25 minutes on the first install on the Amiga brain. It should be much faster on your PC.
cd ~/catkin_ws
catkin_make clean # optionally, clean the workspace
catkin_makeFor: [Method 1]
NOTE: These instructions cover connecting multiple ROS devices to a single ROS master. This is only relevant if you are running the
amiga_ros_bridgeon the Amiga, and connecting other ROS nodes running on your PC to theamiga_ros_bridge.
In order to connect to the same ROS Master when running ROS nodes on multiple devices,
you must specify all nodes to be on the same ROS_MASTER_URI, but with their own ROS_IP.
If you want to connect to the roscore and amiga_ros_bridge running on your Amiga,
you must export the ROS_MASTER_URI and ROS_IP before starting a roscore
and/or before launching or running any node that will connect to that ROS Master.
This would be:
export ROS_MASTER_URI=http://<AMIGA_IP>:11311
export ROS_IP=<AMIGA_IP>Where <AMIGA_IP> corresponds to the IP address seen on the bottom right hand corner of your Amiga brain home screen.
So this command would become, e.g.:
export ROS_MASTER_URI=http://192.168.1.98:11311
export ROS_IP=192.168.1.98Meanwhile, your dev station should be set up to connect to that ROS master.
export ROS_MASTER_URI=http://<AMIGA_IP>:11311
export ROS_IP=<DEV_STATION_IP>Where <DEV_STATION_IP> corresponds to the IP address on your PC running ROS, connected to the same network as the Amiga.
Hint:
<DEV_STATION_IP>can be found withifconfigor other basic tools.
So this command would become, e.g.:
export ROS_MASTER_URI=http://192.168.1.98:11311
export ROS_IP=192.168.1.123For more information see:
For: [Method 1]
The first method is with the amiga_ros_bridge running on the Amiga,
and you connecting other ROS nodes running on your computer to the Amiga's
ROS Master.
Make sure that the Amiga is connected to the same network as your computer and that you know both the IP address of the Amiga and of your PC.
Launch the amiga_ros_bridge on the Amiga by ssh-ing into the ros bridge docker container on the Amiga.
Please contact [email protected] for instructions and credentials.
source ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash
export ROS_MASTER_URI=http://<AMIGA_IP>:11311
export ROS_IP=<AMIGA_IP>
roslaunch amiga_ros_bridge amiga_ros_bridge.launchWhere <AMIGA_IP> corresponds to the IP address seen on the bottom right hand corner of your Amiga brain home screen.
For: [Method 2]
Alternatively, you can run the package in your computer as follows. Make sure that the Amiga is connected to the same network as your computer and that you know the IP address of the Amiga.
roslaunch amiga_ros_bridge amiga_ros_bridge.launch host:=<AMIGA_IP>Where <AMIGA_IP> corresponds to the IP address seen on the bottom right hand corner of your Amiga brain home screen.
For: [Method 3]
Finally, you can run the package in your computer with a mock Amiga canbus server that just echos velocity commands back. To run this, you must first start the mock server in a separate terminal:
Warning: This is experimental and is not guaranteed to work.
This is a stand-in for the actual Amiga gRPC canbus service that echos back the received commands.
In a separate terminal, start the Amiga mock server:
source ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash
cd ~/catkin_ws/src/amiga-ros-bridge/
cargo run --example amiga-mock-serversource ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash
roslaunch amiga_ros_bridge amiga_ros_bridge.launchNow you will be able to connect to the ROS topics used by the amiga_ros_bridge.
Confirm this in another terminal on your PC with:
source ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash
rostopic listNOTE: If running the
amiga_ros_bridgeon the Amiga (as in[Method 1]) and connecting with ROS over the network, make sure to follow the Specifying the ROS Master instructions. Remember to set yourROS_MASTER_URI&ROS_IPbefore running. E.g.,source ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash export ROS_MASTER_URI=http://<AMIGA_IP>:11311 export ROS_IP=<DEV_STATION_IP> rostopic list
And you should see:
/amiga/cmd_vel
/amiga/vel
/rosout
/rosout_aggNOTE: If controlling the robot with a ROS connection over the network, make sure to follow the Specifying the ROS Master instructions.
You can start the experimental amiga-joystick app to command velocities to the Amiga (e.g. the mock server) and print received velocity states:
Warning: This is not stable and may require multiple attempts at launching for this to come up.
source ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash
cd ~/catkin_ws/src/amiga-ros-bridge/
cargo run --example amiga-joystickUse arrow keys (left, right, up, down) to command velocities to the Amiga.
You can publish Twist commands to the ROS bridge on the /amiga/cmd_vel topic with the rqt_robot_steering package.
Install rqt_robot_steering, if needed:
apt-get install ros-noetic-rqt-robot-steeringRun from your terminal:
source ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash
rosrun rqt_robot_steering rqt_robot_steering
# Then change the topic to `/amiga/cmd_vel`You can subscribe to measured TwistStamped states of the amiga with ROS command line tools.
source ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash
rostopic echo /amiga/velWe have provided some examples to help you get started. You will find the examples in the examples directory.
amiga_cmd_vel_publisher.py: Publishes aTwistStampedmessage on the/amiga/cmd_veltopic.amiga_vel_subscriber.py: Subscribes to the/amiga/veltopic and prints the receivedTwistStampedmessages.
amiga_cmd_vel_publisher.rs: Publishes aTwistStampedmessage on the/amiga/cmd_veltopic.amiga_vel_subscriber.rs: Subscribes to the/amiga/veltopic and prints the receivedTwistStampedmessages.amiga-joystick.rs: A simple joystick to command velocities to the Amiga and print received velocity states.
As of March 29, 2023 - the ROS docker container for the Amiga has a built in installation of depthai-ros.
This is installed as the ros-noetic-depthai-ros apt package.
You can install the March 29, 2023 ROS docker container for the Amiga with the same command you used to install the original ROS docker container for the Amiga.
Please refer to depthai-ros on full usage of their ROS package.
As of March 29, 2023 - there is no support for visualization in the ROS docker container for the Amiga.
This means you can use the depthai-ros library to connect to the Oak cameras on your amiga,
use other ROS nodes running on the Amiga for image processing,
but you will need to stream them over a network to a PC to visualize them.
This is done by properly setting ROS_MASTER_URI & ROS_IP on all devices, as explained in Specifying the ROS Master.
NOTE: You must stop the oak camera service(s) in your apps launcher setting page so the
depthai-rospackage can access the Oak camera device(s).
Tips:
- We provide a quick example of using the
depthai-rosto stream images below - It is up to you to read their docs to decide which of their launch files / nodes / examples you want to use
- It is up to you to read their docs to configure / interact with the cameras how you want. E.g.,
- Specify
MxIdof the camera you want to stream - Configure for PoE cameras to reduce expected throughput compared to USB (See: https://github.com/luxonis/depthai-ros#poe-cameras)
- Get camera calibrations
- Pass a Neural Network to run on the Oak
- Etc.
- Specify
Use an example from depthai-ros to stream an oak device.
source /opt/ros/noetic/setup.bash # Or source your catkin_ws
export ROS_MASTER_URI=http://<AMIGA_IP>:11311
export ROS_IP=<AMIGA_IP>
roslaunch depthai_examples stereo_inertial_node.launchWhere <AMIGA_IP> corresponds to the IP address seen on the bottom right hand corner of your Amiga brain home screen.
You will see an error that rviz cannot be launched because there is no support for visualization in this docker container. But, if the Oak camera is available, the
depthai-rosnode will start and a camera will be streaming.ERROR: cannot launch node of type [rviz/rviz]: rviz ROS path [0]=/opt/ros/noetic/share/ros ROS path [1]=/data/home/ros/catkin_ws/src ROS path [2]=/opt/ros/noetic/share
Watch the the stream from a computer on the same network.
source /opt/ros/noetic/setup.bash # Or source your catkin_ws
export ROS_MASTER_URI=http://<AMIGA_IP>:11311
export ROS_IP=<DEV_STATION_IP>
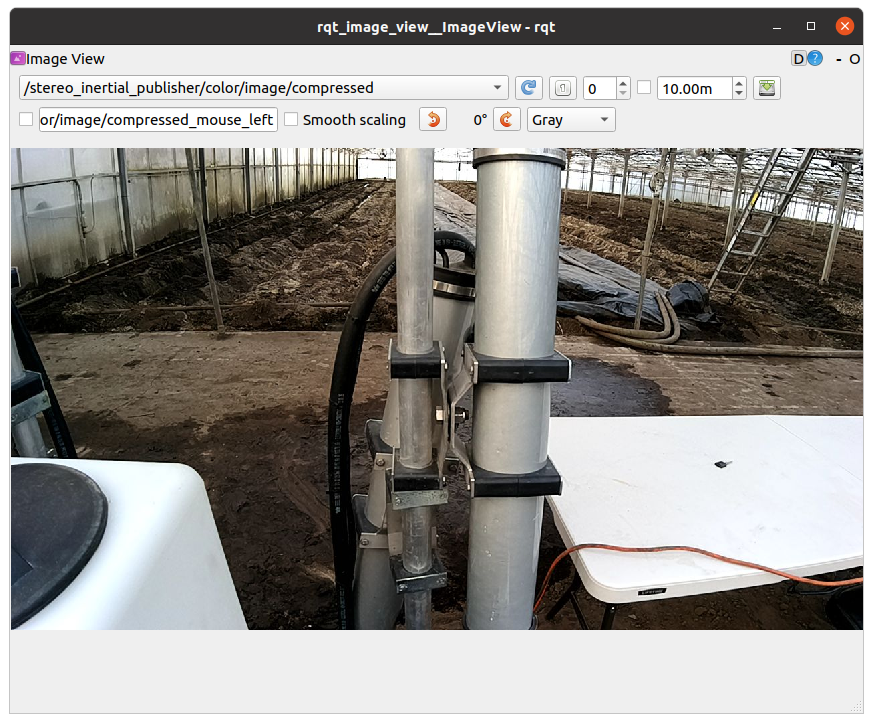
rqt_image_viewWhere <AMIGA_IP> corresponds to the IP address seen on the bottom right hand corner of your Amiga brain home screen.
And <DEV_STATION_IP> corresponds to the IP address on your PC running ROS, connected to the same network as the Amiga.
Now select the image you want to view based on topic, e.g. /stereo_inertial_publisher/color/image or /stereo_inertial_publisher/stereo/depth.
Inspect ci_test.sh for a full example of how to run the bridge in a CI environment.