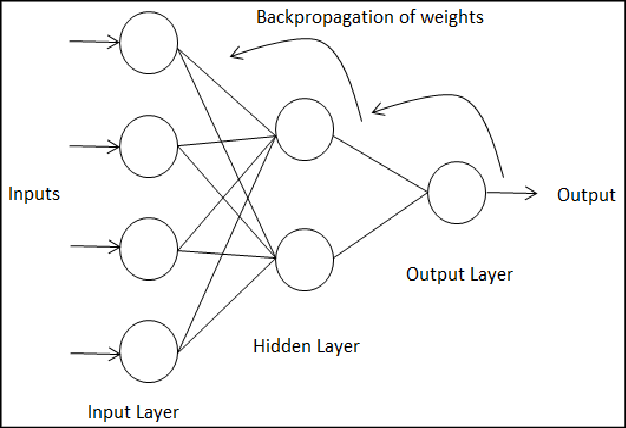
Neural network is a machine learning model which tries to mimic the neurons present in our body, where information in coming from every direction rather than just one in case of conventional models like linear regession, logistic regression, Natural Language Processing,etc. This information is processed by the current perceptron and passed on to next perceptron. This process goes on and on until the output/final layer is reached.
With Neural Networks there is a possibility of complex decision boundaries making it a more efficient non-linear model.
A perceptron is like a neuron which collects information from other neurons processes it and then further pass the preprocessed information. There can be as many perceptron in each hidden layer and each layer can further have different activation functions. Some can have sigmoid, relu function while others can have any tangential function etc, it is totally up to our choice. But generally we use sigmoid and relu as our activation function.
The two main operations while implementing neural networks are:
-
Forward Propagation - Forward propagation is used to evaluate the result of our model / to make predictions. As the name suggests we move from our input layer to the farthest output layer.
-
Backward Propagation - Backward propagation is used to optimize the weights and bias to increase the accuracy of our model. In other terms it is simply implemented to train our neural network.
In contrast to forward propagation we move backwards by pushing the error back to the previous layer and updating the weights along the way.
As told earlier it is used to optimize the weights and bias by pushing the error backwards.The cost function used here can be same as the one used in linear regression.
Generally the cost function used is the mean square error.
The weights and bias can be optimized using gradient descent by taking the derivative of cost function wrt weights and bias.
Let the current position of current perceptron be i and the position of next perceptron be j. The derivative of cost function E wrt to the weight wij can be broken down using total derivatives.
Here Oj is the output of the jth perceptron and similarly inputj is the input to the jth perceptron.
-
Note: input to the jth perceptron contains input from all the perceptrons from the previous hidden layer. Let the number of perceptrons in the previous layer be l.
inputj can be described as :-
$$\sum_{k=1}^l w_{kj} * O_k$$ derivative of inputj wrt wij gives the following and can be further reduced as:
The derivative of Oj wrt to input is equal to the derivative of activation function, which is sigmoid in our case.
The derivative of sigmod is sigmoid(z)(1-sigmoid(z))
-
When j is the output layer perceptrons
In this case output Oj becomes equal to ypredicted.,thus the final derivate in case of j as output layer becomes:
-
When j is not the output layer-In this case the output Oj from the jth perceptron does not directly effect the cost function E. It first affects the input going to the next hidden layer which again affect the inputs of the next hidden layer and this goes on and on.
Thus, the derivative of cost E wrt to Oj depending on the incomming inputs to the nxt hidden layer containing k perceptrons can be written as-
here, derivative of E wrt input is equal to first two derivative terms in the derivative of E wrt Oj+1.
Thus, if we know the first two derivative terms then we can find the derivatives of the previous layer. Since we can easily find out the first two derivative terms for the farthest layer i.e output layer ,we can pass this error backwards to the previous hidden and find their derivative and again send their error backward and continue this process till the first layer.
This is know as backward propagation as we our propagating backwards to optimize the weights.
We have implemented two gates -AND & XOR. Neural network for AND gate contains a single hidden layer while for XOR we have two hidden layers. Each hidden layer contains two perceptrons in addition to a bias.
-
Fit function is used to first generate random weights and bias and then by backpropagation optimizing them to increase the accuracy. This function takes four argumenst-
- X-inputs
- Y-yactual
- lr-Learning rate
- itr-No of iteration to perform backpropagation.
After optimizing the weights and bias it returns the optimized weights and bias.
-
Predict function is used to predict the output by performing forward propagation. It takes the xinputs along with optimized weights and bias generated by fit function as arguments