Let's review some basic commands that you can use to navigate and control the file system:
cd- change directory.mkdir [options] <Directory>- create directory.rmdir [options] <Directory>- remove directory.touch [options] <filename>- create a file.cp [options] <source> <destination>- copy file to another location.mv [options] <source> <destination>- move file to another location.rm [options] <file>- remove file from the fs.cat <filename>- print the content of a given file.
Note: there is no undo! The Linux cli does not have an undo feature. Perform destructive actions carefully.
Use nano or vim.
Note: Although vim is a very powerful editor, throughout the course we will be using nano.
If you don't know vim or nano, please familiarize yourself.
Hidden files
If the file or directory name begins with a . (full stop) then it is considered to be hidden.
myuser@hostname:~$ cd ~
myuser@hostname:~$ ls -l
drwxrwxr-x 4 myuser myuser 4096 Jul 25 2022 aa
-rw-rw-r-- 1 myuser myuser 191005 Feb 7 2022 aaa.pdf
-rw-rw-r-- 1 myuser myuser 60085406 Oct 23 11:05 adobe.deb
...
myuser@hostname:~$ ls -la
drwxrwxr-x 4 myuser myuser 4096 Jul 25 2022 aa
-rw-rw-r-- 1 myuser myuser 191005 Feb 7 2022 aaa.pdf
drwx------ 3 myuser myuser 4096 Oct 23 11:21 .adobe
-rw-rw-r-- 1 myuser myuser 60085406 Oct 23 11:05 adobe.deb
...The above example uses the ls command with the -a flag to include hidden files in the list.
Note the directory .adobe, which is hidden.
By default, ls doesn't print hidden files.
Tip! You can combine multiple options on the same flag: ls -l -a is equivalent to ls -la.
Wildcards are a set of elements that allow you to create a pattern defining a set of files or directories.
Here is the basic set of wildcards:
*represents zero or more characters.?- represents a single character.[]- represents a range of characters.
myuser@hostname:~$ cd /etc
myuser@hostname:/etc$ ls
total 1664
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 ינו 4 14:54 acpi
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 3028 אוג 1 2017 adduser.conf
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 ינו 4 13:29 alsa
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 36864 ינו 4 15:40 alternatives
...
myuser@hostname:/etc$ ls b*
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2320 פבר 4 2021 bash.bashrc
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 45 אוג 12 2015 bash_completion
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 367 ינו 27 2016 bindresvport.blacklist
...The above example prints all files starting with b.
Permissions specify what a particular user may or may not do to a given file or directory. On a Linux system, every file is owned by a user, a group and “others”.
myuser@hostname:~$ ls -l
-rw-rw-r-- 1 myuser users 5 Jan 15 12:39 To_Do
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 45948 Aug 9 15:01 /bin/ls*In the above example, the first file is a regular file (first dash).
Users with username myuser or users belonging to the group users can read and write (change/move/delete) the file, but they can't execute it (second and third dash). All other users are only allowed to read this file, but they can't write or execute it (fourth and fifth dash).
The second example is an executable file, the difference: everybody can run this program, but you need to be root to change it.
On a Linux system there are only 2 people usually who may change the permissions of a file or directory. The owner of the file or directory and the root user. The root user is a superuser who is allowed to do anything and everything on the system.
Linux permissions dictate 3 things you may do with a file, read (r), write (w) and execute (x). They are referred to in Linux by a single letter each.
For every file we define 3 sets of people for whom we may specify permissions.
- user (
u) - a single person who owns the file. (typically the person who created the file but ownership may be granted to someone else by certain users) - group (
g) - every file belongs to a single group. - others (
o) - everyone else who is not in the group or the owner.
Use the chmod command to change file's permissions:
myuser@hostname:~$ ls -l
-rw-rw-r-- 1 myuser users 5 Jan 15 12:39 hello
myuser@hostname:~$ chmod u+x hello
myuser@hostname:~$ ls -l
-rwxrw-r-- 1 myuser users 5 Jan 15 12:39 helloThe logic behind the command:
- Who are we changing the permission for?
[ugoa]- user (or owner), group, others, all - Are we granting or revoking the permission - indicated with either a plus (
+) or minus (-) - Which permission are we setting? - read (
r), write (w) or execute (x).
In Unix-like operating systems, file permissions can be represented in octal form, which is XXX, when X is a number between 0 and 7.
To calculate the octal value of file permissions, look at every 3-tuple (the one for the user, group and others) as a binary number. e.g.
rwx- 111r--- 100rw-- 110
Now convert this number to 10-bases number:
rwx- 111 = 7r--- 100 = 4rw-- 110 = 6
Now simply add up the values for each permission that is granted, and use that as the digit in the corresponding position. For example:
rwxrw-rw- would be represented as 766 in octal notation. 7 for rwx of the user, 6 for rw- of the group, 6 again of rw- for others.
- The standard file permission is determined by the mask for new file creation. The value of this mask can be displayed using the
umaskcommand. Before the mask is applied, a directory has permissions777orrwxrwxrwx, a plain file666orrw-rw-rw-. The umask value is subtracted from these default permissions after the function has created the new file or directory. - A directory gets more permissions by default: it always has the execute permission. If it didn't have that, it would not be accessible. Try this out by chmodding a directory to 644!
umask is subtractive, not prescriptive: permission bits set in umask are removed by default from modes specified by programs, but umask can't add permission bits:
myuser@hostname:~$ umask
0002
myuser@hostname:~$ touch 1.txt
myuser@hostname:~$ ls -l 1.txt
-rw-rw-r-- 1 myuser users 5 Jan 15 12:39 1.txt
myuser@hostname:~$ umask 0003
myuser@hostname:~$ touch 2.txt
myuser@hostname:~$ ls -l 2.txt
-rw-rw-r-- 1 myuser users 5 Jan 15 12:40 2.txtAlthough umask of 0003 results in 663 octal form of file permissions (rw-rw--wx), but umask only remove permissions from the default (664), it can not add permi
Sometimes, you need to execute a command as another user. For example:
myuser@hostname:~$ ls -l
-rw------- 1 john johnsfriends 5 Jan 23 12:39 phone
myuser@hostname:~$ cat phone
cat: phone: Permission deniedIn the above example, your personal user is myuser (according to the name in the prompt), but the file phone is owned by the user john. Not only it is owned by john, according to the file's permissions, only john (or users under the group johnsfriends) can read/write to the file.
The sudo command is short for “switch user and do”. In a single command, you can switch to a specific user, perform a command on behalf of that user, and “return” to your user. Here is an example:
myuser@hostname:~$ sudo -u john cat phone
+91524869328In the above example, we under the hood switched to the user john, executed cat phone on his behalf, then back to our user, myuser. In a single command, quite useful.
According to sudo's help page, if you don't specify a user (using the -u flag), the default user that you are switching to is root.
The root user is the administrative user in a Linux-based operating system, including Ubuntu. The root user has complete control over the system and can perform any operation or command, including modifying system files and processes.
In Ubuntu, the root user is disabled by default for security reasons. Instead, administrative tasks are typically performed using the sudo command. How does it work?
Every user that is a member of a special group called sudo (to be confused with the sudo command, there is also a group called sudo), can use the sudo command to execute commands on behalf of the root user, without actually login to this strong user. Your default linux user is a member of the group sudo.
It's important to exercise caution when using the root user account, as any command or operation executed with root privileges has the potential to cause significant damage to the system if performed incorrectly. It's recommended to use the root user account only when necessary and to carefully consider the potential consequences of each action before executing it.
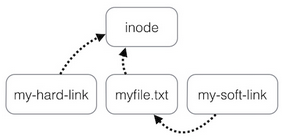
A link is nothing more than a way of matching two or more file names to the same set of file data.
Hard link associates two or more file names with the same inode. Hard links share the same data blocks on the hard disk, while they continue to behave as independent files. Soft link or symbolic link (sometimes pronounced "symlink") is a small file that is a pointer to another file.
Use the ln command to create a hard/soft link:
myuser@hostname:~$ touch myfile.txt
myuser@hostname:~$ ln myfile.txt my-hard-link
myuser@hostname:~$ ln -s myfile.txt my-soft-link