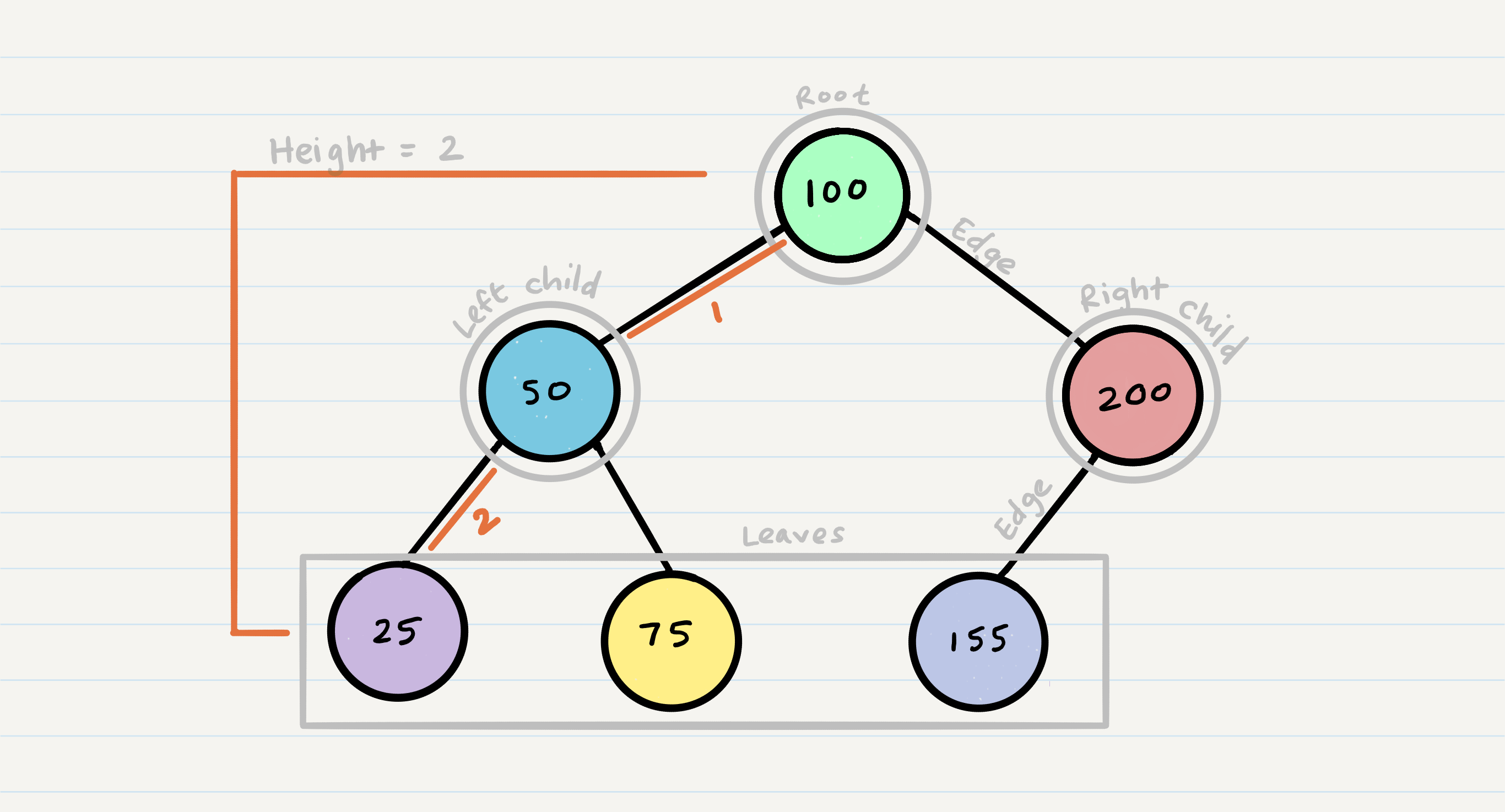
- Node : a tree is combination of nodes that contain values
- Root: the first node in tree
- K : the number of children
- Left : A reference to one child node, in a binary tree
- Right : A reference to the other child node, in a binary tree
- Edge : The edge in a tree is the link between a parent and child node
- Leaf : A leaf is a node that does not have any children
- Height : The height of a tree is the number of edges from the root to the furthest lea
The algorithm starts at the root node (selecting some arbitrary node as the root node in the case of a graph) and explores as far as possible along each branch before backtracking
Pre-order: root >> left >> right
ALGORITHM preOrder(root)
// INPUT <-- root node
// OUTPUT <-- pre-order output of tree node's values
OUTPUT <-- root.value
if root.left is not Null
preOrder(root.left)
if root.right is not NULL
preOrder(root.right)
In-order: left >> root >> right
ALGORITHM inOrder(root)
// INPUT <-- root node
// OUTPUT <-- in-order output of tree node's values
if root.left is not NULL
inOrder(root.left)
OUTPUT <-- root.value
if root.right is not NULL
inOrder(root.right)
Post-order: left >> right >> root
ALGORITHM postOrder(root)
// INPUT <-- root node
// OUTPUT <-- post-order output of tree node's values
if root.left is not NULL
postOrder(root.left)
if root.right is not NULL
postOrder(root.right)
OUTPUT <-- root.value
ALGORITHM breadthFirst(root)
// INPUT <-- root node
// OUTPUT <-- front node of queue to console
Queue breadth <-- new Queue()
breadth.enqueue(root)
while breadth.peek()
node front = breadth.dequeue()
OUTPUT <-- front.value
if front.left is not NULL
breadth.enqueue(front.left)
if front.right is not NULL
breadth.enqueue(front.right)
- Breadth First Traversal
ALGORITHM breadthFirst(root)
// INPUT <-- root node
// OUTPUT <-- front node of queue to console
Queue breadth <-- new Queue()
breadth.enqueue(root)
while breadth.peek()
node front = breadth.dequeue()
OUTPUT <-- front.value
for child in front.children
breadth.enqueue(child)