给定一个数组,它的第 i 个元素是一支给定的股票在第 i 天的价格。
设计一个算法来计算你所能获取的最大利润。你最多可以完成 两笔 交易。
注意:你不能同时参与多笔交易(你必须在再次购买前出售掉之前的股票)。
示例 1: 输入:prices = [3,3,5,0,0,3,1,4] 输出:6 解释:在第 4 天(股票价格 = 0)的时候买入,在第 6 天(股票价格 = 3)的时候卖出,这笔交易所能获得利润 = 3-0 = 3 。随后,在第 7 天(股票价格 = 1)的时候买入,在第 8 天 (股票价格 = 4)的时候卖出,这笔交易所能获得利润 = 4-1 = 3。
示例 2: 输入:prices = [1,2,3,4,5] 输出:4 解释:在第 1 天(股票价格 = 1)的时候买入,在第 5 天 (股票价格 = 5)的时候卖出, 这笔交易所能获得利润 = 5-1 = 4。注意你不能在第 1 天和第 2 天接连购买股票,之后再将它们卖出。因为这样属于同时参与了多笔交易,你必须在再次购买前出售掉之前的股票。
示例 3: 输入:prices = [7,6,4,3,1] 输出:0 解释:在这个情况下, 没有交易完成, 所以最大利润为0。
示例 4: 输入:prices = [1] 输出:0
提示:
- 1 <= prices.length <= 10^5
- 0 <= prices[i] <= 10^5
这道题目相对 121.买卖股票的最佳时机 和 122.买卖股票的最佳时机II 难了不少。
关键在于至多买卖两次,这意味着可以买卖一次,可以买卖两次,也可以不买卖。
接来下我用动态规划五部曲详细分析一下:
- 确定dp数组以及下标的含义
一天一共就有五个状态, 0. 没有操作
- 第一次买入
- 第一次卖出
- 第二次买入
- 第二次卖出
dp[i][j]中 i表示第i天,j为 [0 - 4] 五个状态,dp[i][j]表示第i天状态j所剩最大现金。
- 确定递推公式
需要注意:dp[i][1],表示的是第i天,买入股票的状态,并不是说一定要第i天买入股票,这是很多同学容易陷入的误区。
达到dp[i][1]状态,有两个具体操作:
- 操作一:第i天买入股票了,那么dp[i][1] = dp[i-1][0] - prices[i]
- 操作二:第i天没有操作,而是沿用前一天买入的状态,即:dp[i][1] = dp[i - 1][1]
那么dp[i][1]究竟选 dp[i-1][0] - prices[i],还是dp[i - 1][1]呢?
一定是选最大的,所以 dp[i][1] = max(dp[i-1][0] - prices[i], dp[i - 1][1]);
同理dp[i][2]也有两个操作:
- 操作一:第i天卖出股票了,那么dp[i][2] = dp[i - 1][1] + prices[i]
- 操作二:第i天没有操作,沿用前一天卖出股票的状态,即:dp[i][2] = dp[i - 1][2]
所以dp[i][2] = max(dp[i - 1][1] + prices[i], dp[i - 1][2])
同理可推出剩下状态部分:
dp[i][3] = max(dp[i - 1][3], dp[i - 1][2] - prices[i]); dp[i][4] = max(dp[i - 1][4], dp[i - 1][3] + prices[i]);
- dp数组如何初始化
第0天没有操作,这个最容易想到,就是0,即:dp[0][0] = 0;
第0天做第一次买入的操作,dp[0][1] = -prices[0];
第0天做第一次卖出的操作,这个初始值应该是多少呢?
首先卖出的操作一定是收获利润,整个股票买卖最差情况也就是没有盈利即全程无操作现金为0,
从递推公式中可以看出每次是取最大值,那么既然是收获利润如果比0还小了就没有必要收获这个利润了。
所以dp[0][2] = 0;
第0天第二次买入操作,初始值应该是多少呢?应该不少同学疑惑,第一次还没买入呢,怎么初始化第二次买入呢?
第二次买入依赖于第一次卖出的状态,其实相当于第0天第一次买入了,第一次卖出了,然后在买入一次(第二次买入),那么现在手头上没有现金,只要买入,现金就做相应的减少。
所以第二次买入操作,初始化为:dp[0][3] = -prices[0];
同理第二次卖出初始化dp[0][4] = 0;
- 确定遍历顺序
从递归公式其实已经可以看出,一定是从前向后遍历,因为dp[i],依靠dp[i - 1]的数值。
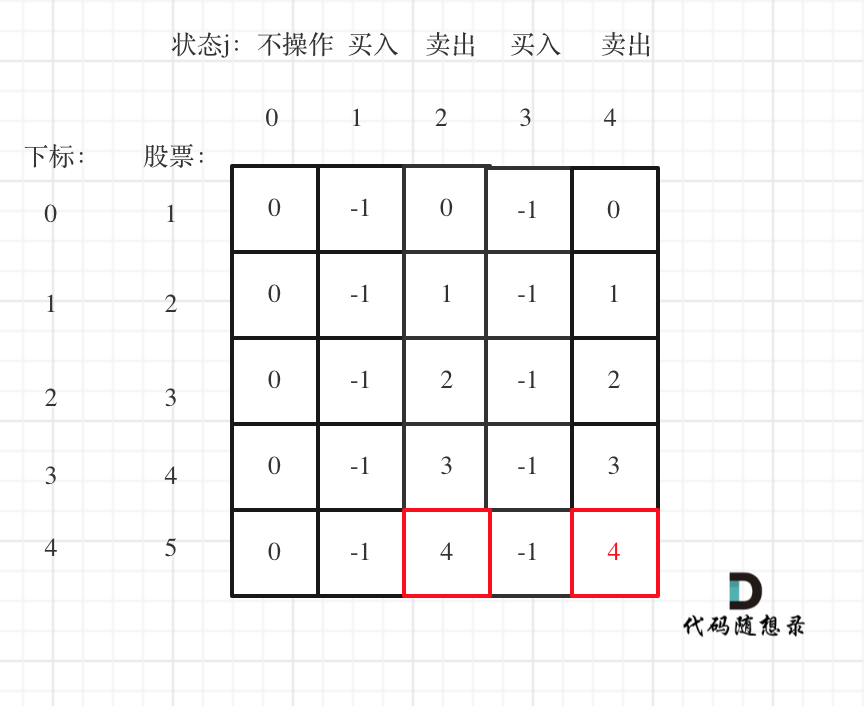
- 举例推导dp数组
以输入[1,2,3,4,5]为例
大家可以看到红色框为最后两次卖出的状态。
现在最大的时候一定是卖出的状态,而两次卖出的状态现金最大一定是最后一次卖出。
所以最终最大利润是dp[4][4]
以上五部都分析完了,不难写出如下代码:
// 版本一
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
if (prices.size() == 0) return 0;
vector<vector<int>> dp(prices.size(), vector<int>(5, 0));
dp[0][1] = -prices[0];
dp[0][3] = -prices[0];
for (int i = 1; i < prices.size(); i++) {
dp[i][0] = dp[i - 1][0];
dp[i][1] = max(dp[i - 1][1], dp[i - 1][0] - prices[i]);
dp[i][2] = max(dp[i - 1][2], dp[i - 1][1] + prices[i]);
dp[i][3] = max(dp[i - 1][3], dp[i - 1][2] - prices[i]);
dp[i][4] = max(dp[i - 1][4], dp[i - 1][3] + prices[i]);
}
return dp[prices.size() - 1][4];
}
};- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(n * 5)
当然,大家可以看到力扣官方题解里的一种优化空间写法,我这里给出对应的C++版本:
// 版本二
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
if (prices.size() == 0) return 0;
vector<int> dp(5, 0);
dp[1] = -prices[0];
dp[3] = -prices[0];
for (int i = 1; i < prices.size(); i++) {
dp[1] = max(dp[1], dp[0] - prices[i]);
dp[2] = max(dp[2], dp[1] + prices[i]);
dp[3] = max(dp[3], dp[2] - prices[i]);
dp[4] = max(dp[4], dp[3] + prices[i]);
}
return dp[4];
}
};- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
大家会发现dp[2]利用的是当天的dp[1]。 但结果也是对的。
我来简单解释一下:
dp[1] = max(dp[1], dp[0] - prices[i]); 如果dp[1]取dp[1],即保持买入股票的状态,那么 dp[2] = max(dp[2], dp[1] + prices[i]);中dp[1] + prices[i] 就是今天卖出。
如果dp[1]取dp[0] - prices[i],今天买入股票,那么dp[2] = max(dp[2], dp[1] + prices[i]);中的dp[1] + prices[i]相当于是尽在再卖出股票,一买一卖收益为0,对所得现金没有影响。相当于今天买入股票又卖出股票,等于没有操作,保持昨天卖出股票的状态了。
这种写法看上去简单,其实思路很绕,不建议大家这么写,这么思考,很容易把自己绕进去!
对于本题,把版本一的写法研究明白,足以!
Java:
// 版本一
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int len = prices.length;
// 边界判断, 题目中 length >= 1, 所以可省去
if (prices.length == 0) return 0;
/*
* 定义 5 种状态:
* 0: 没有操作, 1: 第一次买入, 2: 第一次卖出, 3: 第二次买入, 4: 第二次卖出
*/
int[][] dp = new int[len][5];
dp[0][1] = -prices[0];
// 初始化第二次买入的状态是确保 最后结果是最多两次买卖的最大利润
dp[0][3] = -prices[0];
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) {
dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][1], -prices[i]);
dp[i][2] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][2], dp[i][1] + prices[i]);
dp[i][3] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][3], dp[i][2] - prices[i]);
dp[i][4] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][4], dp[i][3] + prices[i]);
}
return dp[len - 1][4];
}
}
// 版本二: 空间优化
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int len = prices.length;
int[] dp = new int[5];
dp[1] = -prices[0];
dp[3] = -prices[0];
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) {
dp[1] = Math.max(dp[1], dp[0] - prices[i]);
dp[2] = Math.max(dp[2], dp[1] + prices[i]);
dp[3] = Math.max(dp[3], dp[2] - prices[i]);
dp[4] = Math.max(dp[4], dp[3] + prices[i]);
}
return dp[4];
}
}Python:
版本一:
class Solution:
def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int:
if len(prices) == 0:
return 0
dp = [[0] * 5 for _ in range(len(prices))]
dp[0][1] = -prices[0]
dp[0][3] = -prices[0]
for i in range(1, len(prices)):
dp[i][0] = dp[i-1][0]
dp[i][1] = max(dp[i-1][1], dp[i-1][0] - prices[i])
dp[i][2] = max(dp[i-1][2], dp[i-1][1] + prices[i])
dp[i][3] = max(dp[i-1][3], dp[i-1][2] - prices[i])
dp[i][4] = max(dp[i-1][4], dp[i-1][3] + prices[i])
return dp[-1][4]版本二:
class Solution:
def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int:
if len(prices) == 0:
return 0
dp = [0] * 5
dp[1] = -prices[0]
dp[3] = -prices[0]
for i in range(1, len(prices)):
dp[1] = max(dp[1], dp[0] - prices[i])
dp[2] = max(dp[2], dp[1] + prices[i])
dp[3] = max(dp[3], dp[2] - prices[i])
dp[4] = max(dp[4], dp[3] + prices[i])
return dp[4]Go:
func maxProfit(prices []int) int {
dp:=make([][]int,len(prices))
for i:=0;i<len(prices);i++{
dp[i]=make([]int,5)
}
dp[0][0]=0
dp[0][1]=-prices[0]
dp[0][2]=0
dp[0][3]=-prices[0]
dp[0][4]=0
for i:=1;i<len(prices);i++{
dp[i][0]=dp[i-1][0]
dp[i][1]=max(dp[i-1][1],dp[i-1][0]-prices[i])
dp[i][2]=max(dp[i-1][2],dp[i-1][1]+prices[i])
dp[i][3]=max(dp[i-1][3],dp[i-1][2]-prices[i])
dp[i][4]=max(dp[i-1][4],dp[i-1][3]+prices[i])
}
return dp[len(prices)-1][4]
}
func max(a,b int)int{
if a>b{
return a
}
return b
}JavaScript:
版本一:
const maxProfit = prices => {
const len = prices.length;
const dp = new Array(len).fill(0).map(x => new Array(5).fill(0));
dp[0][1] = -prices[0];
dp[0][3] = -prices[0];
for (let i = 1; i < len; i++) {
dp[i][0] = dp[i - 1][0];
dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][1], dp[i - 1][0] - prices[i]);
dp[i][2] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][2], dp[i - 1][1] + prices[i]);
dp[i][3] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][3], dp[i - 1][2] - prices[i]);
dp[i][4] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][4], dp[i - 1][3] + prices[i]);
}
return dp[len - 1][4];
};版本二:
const maxProfit = prices => {
const len = prices.length;
const dp = new Array(5).fill(0);
dp[1] = -prices[0];
dp[3] = -prices[0];
for (let i = 1; i < len; i++) {
dp[1] = Math.max(dp[1], dp[0] - prices[i]);
dp[2] = Math.max(dp[2], dp[1] + prices[i]);
dp[3] = Math.max(dp[3], dp[2] - prices[i]);
dp[4] = Math.max(dp[4], dp[3] + prices[i]);
}
return dp[4];
};